Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
WORLD WAR
I
The treaty that ended World
War I was called the Treaty of
a. | Versailles | c. | Paris | b. | London | d. | World War
I |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which statement is true about
the treaty of Versailles
a. | It put unfair burdens on Poland and
helped created an atmosphere where democracy could not succeed. | c. | It treated all nations the
same. | b. | It was unfair to England and France | d. | It put unfair burdens on Germany and helped created an atmosphere where
democracy could not succeed. |
|
|
|
3.
|
WORLD WAR II
Who was the leader of Germany duing World War
2?
a. | Benito Mussolini | c. | Emporer Hirohito | b. | Joseph Stalin | d. | Adolf Hitler |
|
|
|
4.
|
Who was the leader of Japan duing World War 2?
a. | Adolf Hitler | c. | Joseph Stalin | b. | Emporer Hirohito | d. | Benito
Mussolini |
|
|
|
5.
|
Who was the leader of the Soviet Union duing World War 2?
a. | Emporer Hirohito | c. | Adolf Hitler | b. | Benito Mussolini | d. | Joseph Stalin |
|
|
|
6.
|
Who was the leader of Italy duing World War 2?
a. | Adolf Hitler | c. | Emporer Hirohito | b. | Benito Mussolini | d. | Joseph Stalin |
|
|
|
7.
|
COLD
WAR
Who was the first
leader of the Communist government in Russia?
a. | Lenin | c. | Czar Nicholas | b. | Stalin | d. | Trotsky |
|
|
|
8.
|
What was the iron
curtain?
a. | A political division between Eastern
Europe and Russia | c. | A steel and barbed
wire fence between Germany and the Soviet Union | b. | A division of Europe between the Communist countries in
the East and the free countries in the West. | d. | A division of Europe between the Communist countries in the West and the free
countries in the East |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which country is divided into
four zones after World War II?
a. | Russia | c. | Germany | b. | Soviet Union | d. | France |
|
|
|
10.
|
What was the purpose of the
Marshall Plan?
a. | Help Europe get back on its feet and
prevent mass starvation | c. | Equip an army to
confront the Russians | b. | Help prevent starvation in the Soviet Union | d. | Help to rebuild Eastern Europe and prevent
starvation |
|
|
|
11.
|
The Marshall Plan shows that
America is
a. | a kind, generous and caring
nation. | c. | concerned first
about its military | b. | uncaring and cruel | d. | only concerned about itself |
|
|
|
12.
|
The _____ encouraged North
Korea to invade South Korea.
a. | Communist Chinese and South
Korea | c. | United
Nations | b. | Soviet Union and Communist China | d. | United States |
|
|
|
13.
|
An armistice is an agreement to
stop fighting, it is not really a peace treaty and the nations are technically still at war.
Armistice talks between the North Koreans and the United Nations started in 1951. How long was it
before an armistice was finally signed.
a. | We have a peace treaty in Korea but
no armistice | c. | More than two
years | b. | We still do not have an armistice in Korea | d. | Six months |
|
|
|
14.
|
In 1959, _____ was president of
the United States and _____ was vice president.
a. | Eisenhower -
Nixon | c. | Eisenhower - Von
Braun | b. | Nixon - Eisenhower | d. | Khrushchev - Eisenhower |
|
|
|
15.
|
The Western allies joined
together to form a military organization to defend against Soviet aggression. This army was called
_____
a. | WEST
SETO | c. | NATO | b. | THE MACHINE | d. | EAST NATO |
|
|
|
16.
|
The American, French and
British areas of Berlin were known as _____ Berlin, while the Soviet area of Berlin was known as
_____ Berlin.
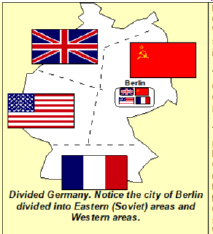
a. | Western -
Eastern | c. | Communist -
Soviet | b. | Communist - Capitalist | d. | Eastern - Western |
|
|
|
17.
|
Why were Soviet missiles in
Cuba a threat to the U.S.
a. | If one of the missiles blew up by
mistake it could destroy Florida | c. | The missiles were not a threat because the U.S. could trust
Cuba | b. | The missiles in Cuba could strike almost any city in the United
States | d. | The missiles were not a threat because the U.S. could
trust the Soviets |
|
|
|
18.
|
Khrushchev agreed to remove
Soviet missiles from Cuba if the U.S. .....
a. | promised not to invade
Turkey | c. | removed its missiles from
Turkey | b. | promised not to invade Cuba | d. | promised not to invade Cuba and removed its missiles from
Turkey |
|
|
|
19.
|
What U.S. president began
America’s involvement in Vietnam?
a. | Nixon | c. | Roosevelt | b. | Kennedy | d. | Johnson |
|
|
|
20.
|
What fact made Vietnam part of
the Cold War and more than just a civil war between Vietnam factions?
a. | All of these facts are
true | c. | The Soviet Union backed North
Vietnam and the Vietcong | b. | The U.S. backed the government of South
Vietnam | d. | The side that eventually took control of Vietnam would put
the communists or the West in a position to take control of the rest of Southeast Asia (domino
theory) |
|
|
|
21.
|
What does Mutual Assured
Destruction mean
a. | Both countries agree that neither
will be destroyed in a war | c. | The country that is attacked will be
destroyed | b. | The country that stats the war will be
destroyed | d. | Both countries who go to war are
guaranteed to be destroyed |
|
|
|
22.
|
The MAD strategy
was
a. | a comic book approach to world
affairs | c. | developed in the
Kennedy administration | b. | a way to prevent war | d. | a guarantee of war |
|
|
|
23.
|
Who was director of the FBI in
the early 1960’s
a. | J. Edgar
Hoover | c. | Bob
McNamara | b. | George Wallace | d. | Orville Faubus |
|
|
|
24.
|
What did President Johnson call
his vision for America?
a. | The Square
Deal | c. | The New
Deal | b. | The Great Society | d. | The Free Society |
|
|
|
25.
|
What was Lyndon Johnson’s
job in the Kennedy administration?
a. | Majority Leader of the
Senate | c. | Minority Leader of the
Senate | b. | Speaker of the House | d. | Vice President |
|
|
|
26.
|
What is the largest communist
nation in the world?
a. | Eastern Europe (including East
Germany) | c. | Soviet
Union | b. | Russia | d. | China |
|
|
|
27.
|
Why did the U.S. place an
embargo on Japan in the 1930’s
a. | Japan was trying to control the TV
business. | c. | Japan invaded
Korea | b. | Japan invaded Chinese Manchuria | d. | Japan was selling too many cars in the
U.S. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which countries supported North
Korea’s attack on South Korea?
a. | The
Soviets | c. | The
Chinese | b. | The Soviets, Chinese and Vietcong | d. | The Soviets and the Chinese |
|
|
|
29.
|
Taiwan used to be called
Formosa. Who controlled Taiwan in the 50’s and still does today?
a. | The Chinese
Communists | c. | The U.S. and
Japan | b. | The North Koreans | d. | The Chinese Nationalists |
|
|
|
30.
|
There is a famous saying,
“Only Nixon Could Go To China.” What does that ;phrase mean.
a. | Nixon was president when the ping
pong team was invited to China | c. | Nixon was not very bright so the Chinese communists trusted
him | b. | The Chinese did not trust Democrats | d. | Since Nixon had the reputation of being an anti-communist, the American people
trusted him to deal with China. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Who, eventually, controlled all
of the land in China?
a. | The
government | c. | The
peasants | b. | The former owners | d. | The capitalists |
|
|
|
32.
|
Why did China attack the U.N
forces in Korea
a. | They did not like the
U.N. | c. | They wanted to use Korea as a
staging area to attack Japan | b. | They wanted to make sure North Korea stayed
communist | d. | They wanted a unified
Korea |
|
|
|
33.
|
Why did American officials
suspect that Jacobo Arbenz might be a communist?
a. | He used land reform to confiscate
farm land the way other communists had done in Cuba and China | c. | Many of his associates were
communist | b. | Neither of these reasons suggest that he is a
communist | d. | Both of these answers are
true |
|
|
|
34.
|
Why did the CIA help to bring
down the Guatemala government?
a. | The U.S. thought that a communist
government in Central America was a threat to U.S. security | c. | Neither of these reasons are
true | b. | The U.S. did not want Che Guevara to take over Guatemala and
Mexico | d. | Both of these are
true |
|
|
|
35.
|
What was the name of the U.S.
policy that said the Europeans had to stay out of the American hemisphere?
a. | The CIA handbook on rules of
engagement | c. | The Emancipation
Proclamation | b. | The Communist Manifesto | d. | The Monroe Doctrine |
|
|
|
36.
|
The events in Chili after
Allende took power most closely resemble the events in _____ after ______
took power
a. | Bolivia - Che
Guevara | c. | China -
Khrushchev | b. | Cuba - Che Guevara | d. | Cuba - Castro |
|
|
|
37.
|
The Marxist economic policies
under Allende
a. | were good for most of the people of
Chili and resulted in prosperity | c. | were a disaster for Chili and helped to cause civil
unrest | b. | would eventually lead to Capitalism | d. | were favored by the U.S. |
|
|
|
38.
|
What was the name of the
Marxist rebel group fighting against the government in Nicaragua?
a. | the Sandinistas | c. | the Somozas | b. | the Contras | d. | the CIA |
|
|
|
39.
|
What was the name of the pro
U.S. leader of Nicaragua who was trying to fight off the Marxist rebels?
a. | Jose
Sandinistas | c. | Somoza | b. | Guevara | d. | Manuael Contra |
|
|
|
40.
|
Why did the U.S. invade
Grenada
a. | Grenada refused to ship oil and
banana’s to the U.S. | c. | Grenada was building an airfield big enough to accommodate Soviet military
aircraft. | b. | Grenada was sending revolutionary agents into the
U.S. | d. | The Grenada army was threatening its
neighbors |
|
|
|
41.
|
What was the money from the
Iran Contra scandal used for?
a. | purchase arms for the Contras in
Nicaragua | c. | make Oliver North
rich | b. | provide funds for the Reagan administration | d. | purchase arms for the Contras in
Cuba |
|
|
|
42.
|
When the people of Nicaragua
were given a chance to vote for the government of their choice they elected
a. | a non-communist
government | c. | a communist
government | b. | a Cuban style government | d. | a pro Soviet government |
|
|
|
43.
|
Who was president of the U.S.
for most of the 1980’s
a. | Jimmy
Carter | c. | Richard
Nixon | b. | Lyndon Johnson | d. | Ronald Reagan |
|
|
|
44.
|
COLD WAR ENDS -
REAGAN
What did Reagan
believe about the health of the Soviet Union?
a. | Soviet communism was weak and ready
to “crackup.”
| c. | It would cost too much money to combat the Soviet
Union
| b. | The U.S. should adapt socialism as its economic
system
| d. | The Soviets were too strong and we
shouldn’t antagonize them
|
|
|
|
45.
|
What is the policy of
“containment?”
a. | The world needs to support
communism | c. | The world needs to
keep communism from spreading any further | b. | The world needs to support
socialism | d. | The world needs to contain
capitalism |
|
|
|
46.
|
There were many anti-communist
forces inside the communist countries. In the past the U.S. Government ignored them. What did Ronald
Reagan do?
a. | He urged them to make peace with
communism | c. | He tried to
suppress these anti-communist movements | b. | He ignored them as previous presidents had
done | d. | He sent them arms to fight their communist
governments |
|
|
|
47.
|
Why was the Pope helpful in the
fight against the communist dictatorship in Poland?
a. | Pope John Paul was Polish. He fought
against the Nazis in World War Two and was highly respected in Poland | c. | The communists liked Pope John
Paul | b. | Pope John Paul was a communist | d. | The Catholic Church had lots of money to
spend |
|
|
|
48.
|
Once a country become
communist, it generally stayed communist. Most presidents accepted the fact that these countries were
communist. What did Reagan do?
a. | He used all of the tactics listed
above to fight communism in the Soviet Union | c. | He sent money to support anti-communist rebels in communist
countries | b. | He forced the Soviets to spend billions of dollars fighting the anti-communist
rebels | d. | He sent military weapons so the anti-communist rebels
could better fight communism |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which statement about
“Star Wars” is true?
a. | The media supported the idea of SDI
(Star Wars) | c. | Even though the
media and Congress thought “Star Wars” was a fantasy that could not work, the Soviets
were afraid of it | b. | The congress supported tie idea of SDI | d. | The Soviets thought SDI was a
fantasy |
|
|
|
50.
|
Which statement below is
true?
a. | The Reagan policies brought an end
to the Cold War | c. | The Reagan
policies brought the world close to World War Three | b. | The Reagan policies caused the Cold War to continue longer
than it had to | d. | Reagan had little or no effect on
the Cold War |
|