Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
Three years after the end of World War II, the Nazis' former capital,
Berlin, would once again find itself the target of an allied air fleet. This time, the air armada was
working to save, rather than destroy, the city.
DIVIDED GERMANY
Following World War II, Germany is divided into four zones of occupation -- Soviet, British,
French and American. Germany, and Berlin in particular, are the only places where communist and
Western forces come into direct contact. | 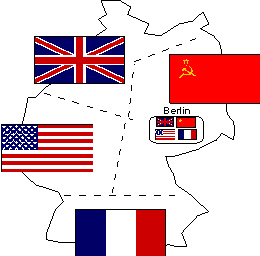 | | |
The city of Berlin is
inside the Soviet sector
and it is also divided into four zones. Three and a half million Berliners live deep inside Soviet
lines. The Nazis' once-proud capital, reduced to a pile of rubble by Allied anger, is down to
its bare essentials. The people of Berlin are starving and the Soviets will not allow the other
nations to come into the city. To get to the city the other nations have to go through the Soviet
zone.
|
|
|
1.
|
How many zones was Germany
divided into after WWII?
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following
countries had zones in Germany
a. | British | d. | French | b. | American | e. | Each of these countries had a zone | c. | Soviet |
|
|
|
3.
|
The city of Berlin was also
divided into four zones. Where was the city of Berlin located?
a. | Inside the British
zone | c. | Inside the Soviet
zone | b. | Inside the American Zone | d. | Inside the French zone |
|
|
|
4.
|
Why was it a problem for the
city of Berlin to be inside the Soviet zone?
a. | The Western allies had to go through
the Soviet zone to get to Berlin | c. | Berlin was the former capital of Germany | b. | There were no good roads into
Berlin | d. | There were many Nazi’s living
there. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Why was Germany, and especially
Berlin, a very dangerous place for world peace in the late 1940’s?
a. | Stalin made a new non-aggression
pact with Germany | c. | The Soviets were
threatening to drop an atomic bomb on the city. | b. | The Nazi’s were still very powerful in Germany and
many Germans wanted a war with the Soviet Union and the Allies | d. | It was the only place where Western and Soviet troops were in direct contact
and any spark could set off a war. |
|
|
|
6.
|
What was the “allied
anger” that reduced the city of Berlin to a pile of rubble?
a. | Missile attacks by the Soviet
Union | c. | Bombing by Moslem
extremists | b. | French troops went on a rampage in Berlin after the
war | d. | Round the clock bombing by Britain and the
U.S. |
|
|
|
CURRENCY
REFORM
In June 1948, an
announcement by the Western Allies brings a crisis to Berlin. They establish a currency reform meant
to wipe out the German black market and further tie the vulnerable German economy to
the West. The Soviets are not told and are infuriated by the action. Moscow says Berlin is located in
the Soviet zone and therefore "economically forms part of it."
Sir Brian Robertson, the
British military governor in Berlin, along with his U.S. counterpart, Gen. Lucius Clay, respond by
introducing a special version of a new German currency, the deutschmark, stamped with a "B"
for Berlin.
|
|
|
7.
|
Why did the Western allies
introduce a new form of money (the deutschmark) into Germany?
a. | help to tie Germany to the West
instead of the Soviets | c. | control the Black
Market | b. | all of these reasons | d. | improve the economy of Germany |
|
|
|
8.
|
The Russians were did not want
the people of Berlin to use the new money because Berlin was in their sector. What did the allies do
to the money used in Berlin to pacify the Russians?
a. | Went back to the old money that
Germany was using. | c. | let the Russians
use Russian money instead of German money | b. | The allies did nothing to pacify the
Soviets | d. | stamped a B on the back of the
money |
|
|
|
AIRLIFT
On Thursday, June 24, 1948, West Berlin wakes to find itself under a Soviet blockade --
and in the midst of the first major confrontation of the Cold War. The Soviets block all of the roads
and railroads so the Allies can not get to the city. The people in Berlin are close to starvation and
there is no fuel to heat their homes. The Western Allies impose a counter-blockade on the Soviet
zone. The Soviets hope to starve the West out of Berlin.
President Truman was faced with a
problem. If the West tried to crash through the Soviet blockade it might set off a new war. If we do
nothing the city of Berlin will come under the domination of the Communists.
The
West had been through a similar short-term Soviet blockade of Berlin two months earlier
-- and had responded with an airlift using air corridors set up in a 1945 agreement with the Soviets.
President Truman vows that we will not be driven out of Berlin. New plans are drawn up -- for
long-term replenishment of West Berlin from the air. The Berlin Airlift has
begun.
|
|
|
9.
|
How did the Soviets blockade
the city of Berlin?
a. | closed all air traffic to the
city | c. | sent tanks to attack the Western
Allies | b. | closed all roads and railroad traffic | d. | the Soviets did not blockade
Berlin |
|
|
|
10.
|
Why didn’t the Western
Allies just wait it out until the Soviets got tired of blocking traffic to the
city?
a. | the people of Berlin wanted to be
part of the Communist block | c. | the people of Berlin were starving and there was no fuel for
heating | b. | the Soviets were getting ready to attack with their superior tank
force. | d. | the Western Allies had no
patience |
|
|
|
11.
|
Who made the decision to send
supplies into Berlin by airplane?
a. | Winston
Churchill | c. | Joseph
Stalin | b. | The French | d. | Harry Truman |
|
|
|
12.
|
Why was President Truman
concerned about the Berlin blockade by the Soviet Union?
a. | The people of Berlin were
starving | c. | There was a chance
of a new World War with the Soviets | b. | The people of Berlin had no fuel | d. | Truman was concerned about all of
these. |
|
|
|
13.
|
When did the Berlin blockade
start
a. | June,
1948 | c. | July,
1945 | b. | June, 1949 | d. | August, 1946 |
|
|
|
NEW
ALLIES
The Berlin
airlift brings a new mindset to the Western Allies, who start thinking of West Germany as an
ally, rather than an occupied territory. In West Berlin, the airlift brings people sustenance and
hope. In one memorable instance, the airlift -- in the form of American pilot Gail Halvorsen -- rains
candy on West Berlin's desperate children.
As it becomes evident that the Soviets are not
going to back down from their blockade, the Western Allies consider how to expand their airlift
operations. Larger cargo planes are brought in, as well as bombers with cargo
capacity
|
|
|
14.
|
What was the important new
attitude in the West caused by the Berlin blockade?
a. | The West started to think of Germany
as a new ally rather than an occupied country. | c. | The West got tired of helping the people of
Europe | b. | The West got tired of helping the German people
| d. | Americans wished they had just backed down when the
Soviets blocked Berlin |
|
|
|
15.
|
When the Soviets refuse to back
down from the blockade, what do the Americans do?
a. | Try to find a way out of the
situation | c. | Order bigger
planes to expand the airlift | b. | Give up and withdraw their troops | d. | Ask the French to take over the
airlift |
|
|
|
16.
|
What does the airlift bring to
the German people in Berlin?
a. | fear and
starvation | c. | anger and
resentment against the West | b. | food and optimism | d. | hatred of Americans |
|
|
|
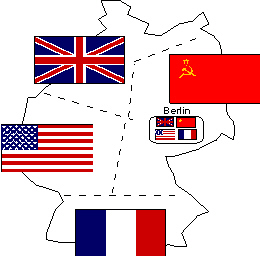 | WEST-EAST
Berliners are still free to move around their city,
despite the Soviet blockade. While West Berlin is suffering through shortages of electricity and
other essentials, the eastern sector offers a relatively normal lifestyle. Politically, however, the
city is on edge.
Soviet troops harass West Berliners who go to the eastern zone.
And in September, a communist attempt to take over the city council sparks mass protests -- which end
in violence. It is obvious that the people of West Berlin do not want to be part of the Soviet
Bloc | | |
|
|
|
17.
|
How is life in West Berlin
during the blockade?
a. | the same as life in East Berlin
(Russian Sector) | c. | Peaceful and
quiet | b. | Hard - little food, fuel or energy | d. | Happy - go - lucky |
|
|
|
18.
|
Why is Berlin on
edge,politically, during the blockade?
a. | The German political parties hate
each other. | c. | The Soviets are
trying to take over the city and make it part of the Communist bloc | b. | Germans do not like
politics | d. | The city is not on edge
politically |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is true about the people
of Berlin”
a. | They want to be part of the Soviet
bloc | c. | They do not like
Americans | b. | They want to be part of the Western bloc | d. | They fear Americans |
|
|
|
20.
|
How did the Soviet troops treat
the people of West Berlin?
a. | The troops harassed
them | c. | They ignored
them | b. | With kindness and understanding | d. | Soviet troops were not near the people of West
Berlin. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Look at the map above. The
Soviet flag is at the
a. | bottom of the
map | c. | middle left of the
map | b. | top left of the map | d. | top right of the map |
|
|
|
22.
|
Look at the map above. The
British flag is at the
a. | bottom of the
map | c. | top left of the
map | b. | top right of the map | d. | middle left of the map |
|
|
|
BLOCKADE
ENDS
The Soviet
Union ends its blockade of Berlin on May 12, 1949. A month earlier, at the
airlift's peak, Western cargo planes were landing at one of Berlin's three airports at a
rate of one every 62 seconds. By the time the airlift ended, more than 275,000 flights had carried
2.3 million tons of supplies to Berlin -- an effort that went down in history as an aviation and
logistical feat.
At least 79 people, including 31 Americans, 39 British and nine Germans, had lost
their lives, mostly in plane crashes. But the confrontation proved to be only the opening act in the
decades-long Cold War.
|
|
|
23.
|
Was the Berlin Airlift
successful?
a. | yes | c. | Can’t tell from the
text. | b. | no |
|
|
|
24.
|
The Berlin
airlift
a. | marked the end of the Cold
War | c. | was not part of the Cold
War | b. | marked only at the beginning of the Cold War | d. | was caused by the Germans |
|
|
|
25.
|
The Berlin
airlift
a. | was a victory for the
Soviets | c. | was a victory for
the Americans | b. | was a defeat for the West | d. | was a defeat for West Berlin |
|