Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
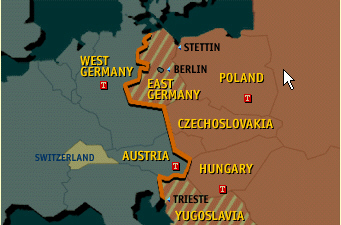 | In the months following their victory in World War II, the alliance between
the Soviet Union and the West quickly proves to be little more than a marriage of convenience.
Suspicion clouds relations -- while a curtain descends over Europe. Concerned about the expansion
of a Communist dictatorship across much of Europe, Winston Churchill first used the term, “Iron
Curtain”, in a speech in President Truman’s home town in Missouri. People listened to
Churchill because he was one of the first to warn the world about Adolf Hitler and Nazi
Germany
| | |
|
|
|
1.
|
Who imposed an “Iron
Curtain” across Europe
a. | Germany | c. | The Allies | b. | Poland | d. | The Soviet Union |
|
|
|
2.
|
What was the “marriage of
convenience” between the Soviet Union and the West?
a. | Working together to defeat Germany
in WWII | c. | Working together
to defeat Germany in the Cold War | b. | Working together to defeat Germany in WWI | d. | Working together to enforce the Treaty of
Versailles |
|
|
|
3.
|
 What country
was Winston Churchill from? What country
was Winston Churchill from?a. | Missouri | c. | France | b. | The U.S. | d. | Great Britain |
|
|
|
4.
|
What was the iron
curtain?
a. | A steel and barbed wire fence
between Germany and the Soviet Union | c. | A division of Europe between the Communist countries in the East and the free
countries in the West. | b. | A political division between Eastern Europe and
Russia | d. | A division of Europe between the Communist countries in
the West and the free countries in the East |
|
|
|
5.
|
After the Iron Curtain was
imposed in Europe, which country found itself living under a Communist
dictatorship?
a. | West
Germany | c. | Austria | b. | East Germany | d. | None of these |
|
|
|
HOMECOMINGS
The United States
emerges from World War II with both its government and economy intact. In fact, the American war
machine has revitalized the nation's businesses and brought affluence to more people on levels
unimaginable during the pre-war Depression. Many Americans have more money to spend because people
worked long hours in defense plants during the war and there was nothing to spend money on. No new
homes were built, no new cars were manufactured and there was rationing on most consumer
goods.
England is a small country and suffered from German bombing. France surrendered to Germany
early in the war and suffered little, except for some towns and villages after the D Day invasion.
The nations that suffered most were Germany and the Soviet Union. Millions died in both countries and
their nations infrastructure was in ruins. The infrastructure of a nation includes such things as
railroads, bridges, mines, factories, and roads.
|
|
|
6.
|
After WWII most Americans found
themselves
a. | better off
financially | c. | about the same
financially as they were before the war | b. | worse off financially | d. | with a great deal of debt because of credit
purchases |
|
|
|
7.
|
Why was the American
infrastructure left unharmed after WWII?
a. | Americans had
rationing | c. | The continental
U.S. was never bombed or attacked | b. | American factories were manufacturing war
goods | d. | America was a Capitalist
country |
|
|
|
8.
|
When was the Great
Depression?
a. | post World War
II | c. | during World War
II | b. | pre World War
II | d. | during the Cold
War |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which countries suffered most
during World WarII?
a. | U.S. and Great
Britain | c. | Germany and
Russia | b. | France | d. | France and
Germany |
|
|
|
CONQUERED,
DIVIDED
Germany, which had
terrorized and occupied much of the European continent, now finds itself divided among the victors.
Four occupation zones are established, and each of the Allies sets up a sector in Berlin.
Meanwhile, national borders are being redrawn in an attempt to settle old scores. Millions of
ethnic Germans are expelled from Poland, Czechoslovakia and Hungary.
|
|
|
10.
|
Which country is divided into
four zones after World War II?
a. | France | c. | Soviet Union | b. | Russia | d. | Germany |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which German city was divided
into four zones after WWII?
a. | Hamburg | c. | Belgrade | b. | Berlin | d. | Stalingrad |
|
|
|
SOVIET
CONTROL
New power struggles spring up in many European
countries following World War II, as communist and capitalist factions vie for control. The most
notable and brutal example of these is the drawn-out civil war in Greece.
Many Americans are concerned because it seemed that the
Soviet Union was extending its control over all of Eastern Europe. The Soviets were taking advantage
of the political and social upheaval, brought about by World War II, to agitate for Communist
revolutions throughout the world. World Communism was a continuation of the policy that the Soviet
Union had before World War II.
|
|
|
12.
|
Why were Americans concerned
with the events in Europe after World War II?
a. | Communist Russia was seizing control
in many European Countries and setting up dictatorships | c. | The Soviets were threatening to revive the Nazi’s in
Germany | b. | The Soviet Union was setting up democratic governments in many places in
Europe | d. | France refused to support us in the United
Nations |
|
|
|
13.
|
What kind of government did the
Soviet Union have?
a. | Democracy | c. | Totalitarian Dictatorship | b. | Democratic Socialist | d. | Democratic Communist |
|
|
|
14.
|
Political and social conflict
can often lead to ______ . This is was happened in Germany after World War I and what happened in
many places throughout the world after World War II.
a. | democracy | c. | freedom | b. | totalitarianism | d. | stability |
|
|
|
WARNINGS
Comments by Stalin in early 1946, that capitalism and imperialism made future
wars inevitable, set off alarm bells in the West. George Kennan, a career U.S. diplomat in Moscow,
was asked by the State Department for his view on Soviet motives and intentions. His famous cabled
response warned there could be no permanent, peaceful coexistence with the Soviet Union.
Days
after Kennan's telegram, Winston Churchill, the former British prime minister, arrives in the
United States. He later speaks at a college in Fulton, Missouri, the home state of his host, U.S.
President Harry Truman. It coined the phrase that best described the political and ideological divide
between the Soviets and the West as the Cold War began.
|
|
|
15.
|
Who said that because of
capitalism and imperialism, future war with the Soviet Union is inevitable?
a. | Joseph Stalin, leader of Great
Britain | c. | Joseph Stalin,
leader of Soviet Russia | b. | George Kennan | d. | Winston Churchill |
|
|
|
16.
|
The comments by Joseph Stalin
in 1946 showed that
a. | he wanted peaceful
coexistence | c. | he saw the U.S. as
an enemy | b. | he wanted war with the U.S. as soon as
possible. | d. | he wanted friendship with the
U.S. |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the phrase that best
described the political and ideological divide between the Soviets and the West and signaled the
start of the Cold War.
a. | Steel
Curtain | c. | Partition of
Germany | b. | Iron Curtain | d. | Berlin Wall |
|
|
|
18.
|
Moscow is the capital of what
country?
a. | Poland | c. | East Germany | b. | Germany | d. | Soviet Union |
|
|
|
TRUMAN'S
DOCTRINE
Churchill's "Iron Curtain" speech
set the tenor for the growing tensions between the Soviet Union and its former allies.
The chill
in relations between communism and the West coincides with the unusually bitter winter of 1946-47. As
shortages and famine gripped an exhausted Europe, President Truman announced what became known as the
Truman Doctrine.
The Truman Doctrine was first established in 1947 after Britain no longer could
afford to provide anti-communist aid to Greece and Turkey, it pledged to provide U.S. military and
economic aid to any nation threatened by communism.
|
|
|
19.
|
Shortages, famine and the cold
winter benefited
a. | the U.S. who wanted to keep the
European countries suppressed and under control | c. | the Soviet Union who wanted to foment communist revolutions in
Europe | b. | the British who wanted to maintain control of its European
colonies | d. | Germany who was evolving as a new
economic super-power in Europe |
|
|
|
20.
|
From this passage, we can infer
that
a. | Truman respected
Churchill | c. | Truman feared
Churchill | b. | Churchill feared Truman | d. | Truman and Churchill were suspicious of each
other. |
|
|
|
21.
|
From this passage we can infer
that
a. | The U.S., Britain, and Greece were
allies | c. | The U.S. and Britain were
allies | b. | The U.S. Britain and Turkey were allies | d. | The U.S., Britain, and Russia were
allies |
|