|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
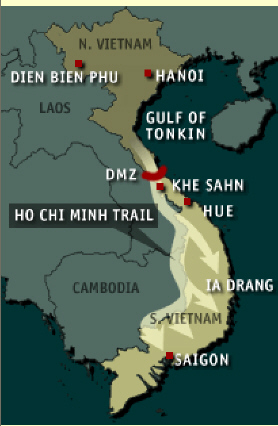 | It was a conflict that devastated one nation and divided another. Vietnam
brought a new dimension to the Cold War -- and forced the United States to rethink its goals in the
superpower rivalry.
DIVIDED
For eight years, Vietnam was a colonial battleground -- as France
fought a nationalist movement led by Ho Chi Minh. Despite financial backing from the United States,
the French lost control of Vietnam in 1954 -- after a Vietnamese force captured the French outpost at
Dien Bien Phu.
An international peace conference in Geneva temporarily divided Vietnam into a
communist-led North and non-communist South and agreed that countrywide elections would be held in
1956. America opposed the elections, fearing the communists would gain control. The elections were
never held.
| | |
|
|
|
1.
|
The names of the two countries
to the West of Vietnam, through which parts of the Ho Chi Minh trail went were named _____ and
_____
a. | Burma -
Vietnam | c. | Thailand -
Laos | b. | China - Laos | d. | Laos - Cambodia |
|
|
|
2.
|
Saigon was the capital of
a. | North
Vietnam | c. | The
DMZ | b. | South Vietnam | d. | Laos |
|
|
|
3.
|
Hanoi was the capital of
a. | North
Vietnam | c. | Cambodia | b. | South Vietnam | d. | Laos |
|
|
|
4.
|
What was the final battle that
drove the French out of Vietnam?
a. | Ho Chi
Minh | c. | the battle of la
Drang | b. | the battle of Hue | d. | Dien Bien Phu |
|
|
|
DIVIDED
For eight years, Vietnam was a colonial battleground -- as
France fought a nationalist movement led by Ho Chi Minh. Despite financial backing from the United
States, the French lost control of Vietnam in 1954 -- after a Vietnamese force captured the French
outpost at Dien Bien Phu.
DMZ
Vietnam's Demilitarized Zone was established in
1954 at the Geneva conference -- which created Vietnam from the former French colony of Indochina. It
was meant to be a temporary divide between the rival governments in the north and south of the
country -- a six-mile-wide buffer zone. But the DMZ soon became the de facto border between the
communist North and the Catholic South Vietnam.
| | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
What was the name of the divide
between North and South Vietnam
a. | 38th
parallel | c. | Communist
divide | b. | Ho Chi Minh Trail | d. | Demilitarized Zone DMZ |
|
|
|
6.
|
Communism preaches atheism and
they have been persecuting Catholics for a long time. At one time a large percentage of the
Vietnamese people were Catholics and Vietnam’s Catholics were afraid of the communists. After
1955, where did most of the Vietnamese Catholics reside?
a. | Laos | c. | South Vietnam | b. | Cambodia | d. | North Vietnam |
|
|
|
IRON FISTS
The North Vietnamese embarked on radical land reforms,
persecuting and imprisoning landowners and aggravating a refugee crisis. By 1955, close to a million
people had fled south.
In South Vietnam, the United States supported the regime of President Ngo Dinh Diem, a catholic
anti-communist determined to resist Hanoi. To fight Diem and unite Vietnam under the Hanoi
government, the communists in 1960 created the National Liberation Front -- the guerrilla
organization also known as the Viet Cong.
Groups such as the Viet Cong were encouraged by Moscow.
U.S. President John F. Kennedy, after suffering a setback against the communists in Cuba and trying
to control the crisis in Berlin, wanted to show U.S. resolve in Asia. He sent American military
advisers to South Vietnam. His advisors, including Robert McNamara, began early to organize and
plan U.S. operations in Vietnam.
| |
|
|
|
7.
|
What U.S. president began
America’s involvement in Vietnam?
a. | Kennedy | c. | Nixon | b. | Johnson | d. | Roosevelt |
|
|
|
8.
|
Who was the leader of South
Vietnam in the early 60’s?
a. | Ho Chi
Minh | c. | Ngo Dinh
Diem | b. | Cho En Lai | d. | Dien Biem Phu |
|
|
|
9.
|
What fact made Vietnam part of
the Cold War and more than just a civil war between Vietnam factions?
a. | The Soviet Union backed North
Vietnam and the Vietcong | c. | The side that
eventually took control of Vietnam would put the communists or the West in a position to take control
of the rest of Southeast Asia (domino theory) | b. | The U.S. backed the government of South
Vietnam | d. | All of these facts are
true |
|
|
|
10.
|
Why did millions of
people flee from the North to South Vietnam
a. | escape from capitalist
reforms | c. | better farming in
the South | b. | escape from communism | d. | escape the North Vietnam draft |
|
|
|
OVERTHROW
Diem's attempts to control the Viet Cong grew more
extreme and created growing discontent in South Vietnam. Several monks burned themselves to death as part of
public protests against the Diem regime.
A group of Diem's generals turned against him.
On November 1, 1963, they attacked the Presidential Palace, believing they had or would have American
support. By the next day, the government was overthrown and Diem was dead, murdered by his own
soldiers.
While the people of Saigon initially responded with enthusiasm to Diem's
overthrow, the coup left the country with no clear leader
| 
Diem - First
President of South Vietnam | | |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following
statements is true
a. | Diem was a communist and would have
turned the country over to the North | c. | The death of Diem and his family made the leadership of North Vietnam
weak | b. | The death of Diem and his family left a power vacuum in South Vietnam with no
clear leader. | d. | The generals who took over after
Diem unified the country in strong opposition to the
North |
|
|
|
12.
|
The generals who overthrew and
murdered Diem had the support of
a. | the Johnson
Administration | c. | the Nixon
Administration | b. | the Kennedy Administration | d. | no American government officials |
|
|
|
GULF OF
TONKIN
Within weeks of
Diem's murder, President Kennedy was assassinated.
Vice President Lyndon Johnson assumed office determined
not to lose Vietnam to the communists. He kept former President Kennedy’s foreign policy
advisors. He sent Defense Secretary Robert McNamara to South Vietnam to re-pledge U.S. support.
In August 1964, the USS Maddox, an American destroyer on patrol in the Gulf of Tonkin,
exchanged fire with North Vietnamese torpedo boats. Two days later, the ship's captain reported
he was under attack again. Despite conflicting evidence, the Pentagon insisted there had been a
second unprovoked attack.
The incident prompted Johnson to push the Gulf of Tonkin
Resolution through Congress. The measure allowed LBJ to wage war in
Vietnam | 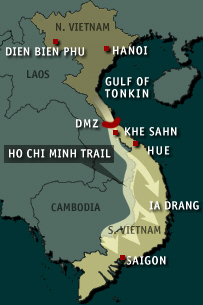 | | |
|
|
|
13.
|
Why did President Johnson push
for the Gulf of Tonkin resolution?
a. | He wanted to unify support in
Vietnam for the U.S. | c. | He wanted the
support of Congress so he could take further military action in
Vietnam | b. | He wanted North Vietnam to give us a naval
base | d. | He wanted the support of the former Kennedy administration
and the people of South Vietnam |
|
|
|
14.
|
Robert McNamara was a key
player in the Vietnam war. Who was he?
a. | U.S. Secretary of
State | c. | Democratic Council
Chairman | b. | U.S. National Security Advisor Chairman | d. | U.S. Secretary of Defense |
|
|
|
15.
|
Where is the Gulf of
Tonkin?
a. | South
Vietnam | c. | International
Waters | b. | Southern China | d. | North Vietnam |
|
|
|
16.
|
Who was president when the Gulf
of Tonkin incident took place?
a. | Kennedy | c. | Nixon | b. | Johnson | d. | McNamara |
|
|
|
ESCALATION
In March 1965, four months after Johnson was elected
president by a landslide, the first
U.S. ground troops landed at Da Nang.
Johnson was convinced that, without the support of a
massive U.S. force, South Vietnam was doomed. In response to the U.S. troop buildup, North Vietnam
began to send thousands of soldiers to fight in South Vietnam. In the Ia Drang valley in
Vietnam's central highlands, the North Vietnamese and U.S. armies met in the first major battle
of the war. It was an American victory -- but U.S. casualties were heavy.
American GIs,
meanwhile, found themselves in a baffling war. They were unable to distinguish friend from
foe. American bombing and shelling drove tens of thousands of Vietnamese from their villages.
American television networks kept a running tally of the U.S. "body count."
Johnson
attempted to force the North Vietnamese to the negotiating table by bombing North Vietnam --
including the Ho Chi Minh Trail, the primitive but highly effective supply line that linked North
Vietnam with its fighters and supporters in the South. But the tactic
failed
| |
|
|
|
17.
|
Why didn’t President
Johnson give military aide to the South and let them fight the war on their own?
a. | Congress was angry and wanted war
| c. | Johnson was a “war
monger” | b. | He did not think the South could win on their
own | d. | Johnson was a catholic and hated North
Vietnam |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which statement is
true
a. | Because the Vietcong hid among the
civilian population, the U.S. was forced to bomb many Vietnam villages and
farms | c. | The U.S. lost its first encounter
with the communists at the battle of Phu | b. | The U.S. won its first encounter with the Communists at Dien Bien
Phu | d. | all of these statements are
true |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is
“Escalation”
a. | Every time one side builds up its
forces, the other side builds up its forces too | c. | The Ho Chi Minh trail | b. | The body count goes higher and
higher | d. | Verbalization |
|
|
|
20.
|
In 1965, President Johnson
a. | had only weak support in the
U.S. | c. | decided to resign from
office | b. | was very unpopular because of the war | d. | was very popular in the United
States |
|
|
|
21.
|
Who was president with the war
ended in Vietnam
a. | Johnson | c. | Nixon | b. | Kissinger | d. | McNamara |
|
|
|
QUAGMIRE
The growing scale and savagery of the war in Vietnam
created growing dissent back in the United States. Johnson was politically weakened by the anti-war movement.
In 1968,
communist forces launched wide-scale attacks throughout South Vietnam to coincide with Tet, the
Vietnamese new year. The communists hoped to spark a general uprising across the country, a mission
that ultimately failed. But the strength of the offensive came as a shock to the American public and
Johnson.
He offered to begin peace talks with the North Vietnamese -- and announced he would not
run for another term in office.
In May 1968, peace talks began in Paris but soon deadlocked.
Richard Nixon, who had begun his campaign for the presidency, called for an "honorable"
end to U.S. military involvement in Vietnam. The North wanted full control of the South and the
U.S. believed it could not abandon South Vietnam. The war was to last another four years, costing
thousands more lives. President Nixon sent Henry Kissinger to negotiate with the North and a peace
treaty was eventually signed.
| |
|
|
|
22.
|
What was the
“quagmire” in Vietnam?
a. | The use of body count to measure the
success of the war | c. | Getting bogged
down in a long “never ending” war | b. | The request for peace talks in Quagmire
France | d. | The use of guerilla tactics by the
North |
|
|
|
23.
|
If the U.S. was supplying and
helping South Vietnam, who was helping and supplying North Vietnam?
a. | France and Soviet
Union | c. | China and
Laos | b. | Soviet Union and Cambodia | d. | Soviet Union and China |
|
|
|
24.
|
Why did the peace talks drag on
for so long?
a. | The U.S. did not want to sacrifice
the people of South Vietnam to the North | c. | The North did not want to return U.S.
prisoners | b. | North Vietnam wanted large sums of money from the U.S.
| d. | The South wanted more territory in the
North. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The Tet Offensive
was
a. | a psychological loss but a military
success for the North | c. | a military defeat
but a psychological victory for the North | b. | a psychological success and a military success for the
South | d. | a military success and a psychological success for the
North |
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | 
Henry
Kissinger | e. | 
Robert McNamara | b. | 
Ngo Dinh
Diem | f. | 
Ho Chi
Minh | c. | 
Lyndon
Johnson | g. | 
Richard
Nixon | d. | 
General William
Westmorland | h. | 
John F
Kennedy |
|
|
|
26.
|
Kennedy Secretary of Defense
who went to work for the Johnson administration and was the main architect of the war in
Vietnam
|
|
|
27.
|
In charge of American Military
forces in Vietnam
|
|
|
28.
|
Leader of North
Vietnam
|
|
|
29.
|
President of South Vietnam,
who was assassinated in a coup
|
|
|
30.
|
Nixon’s foreign policy
advisor who finally negotiated an end to the Vietnam war
|
|
|
31.
|
President of the U.S. who is
identified with the Vietnam war
|
|
|
32.
|
President who finally ended
the Vietnam War
|
|
|
33.
|
This President was in office
when the Vietnam war started
|