|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
Examine the introduction above.
Explain what you expect to learn in this lesson. Also, review the vocabulary words and look for them
as we go through this lesson. You will be tested on them later.
|
|
|
America’s economy is big—very big. It consists of roughly 108 million
households of about 288 million people who work at some 137 million jobs and earn more than $8
trillion a year. They make savings deposits of $28 billion or so in about 71,000 banks. They buy
close to 6.5 million homes and 17 million automobiles a year.
The economy goes through regular
periods of recession and recovery. Some recoveries take longer than others because of bad government
policies, but over time the total economy in the U.S. tends to trend up, or improve.
In
Washington, armies of economists use the latest computer and other technologies to try to predict
whether this massive economy will grow or shrink. Economic policymakers pull in the reins when the
economy bolts at breakneck speed, and attempt to kick start it when it gets slow and
unproductive.
|
|
|
2.
|
Though the American economy
goes through regular cycles what is the over-all trend of the economy?
a. | The American economy
improves | c. | The American
economy declines | b. | The American economy remains stagnant | d. | The economy trends up sometimes and trends down
sometimes |
|
|
|
3.
|
Government economists use
various tools to ensure that the economy
a. | always grows as much and as fast as
it can | c. | grows at a moderate steady
pace | b. | always runs at a slow pace | d. | remains static and with no
growth |
|
|
|
Tracking
Business Cycles
In this
section we’ll examine how the United States government affects macroeconomic
trends.
Macroeconomics is the study of the behavior and decision making of entire economies. This
branch of economics examines major trends for the economy as a whole. Microeconomics, in
contrast, is the study of the economic behavior and decision making of small units, such as
individuals, families, households, and businesses. (Macro means “large,” while
micro means “small.”)
One way economists measure economic well-being is by
calculating the nation’s
gross domestic product (GDP), the total value of all final
goods and services produced in an economy. Economists follow the
country’s GDP and other key
statistics to
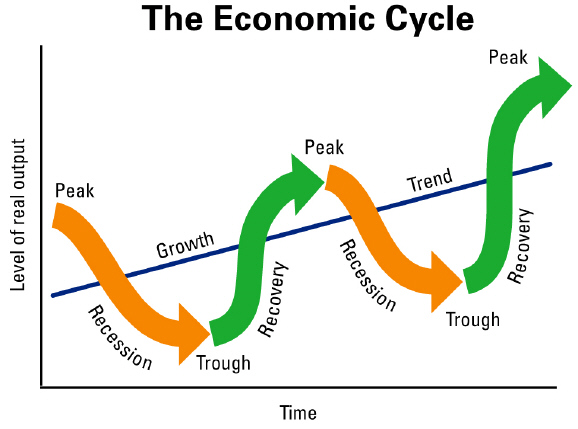
predict business cycles. A business cycle is
a period of macroeconomic
expansion
followed by a period of contraction, or decline. These economic cycles are major
fluctuations, unlike the day-to-day ups and downs of the stock market. We are always at some point in
the business cycle. Cycles may last less than a year or continue for many
years. | Free enterprise systems are subject to
business cycles because economic
decisions
about factors such as prices, production,
and consumption are made by
individuals
and businesses acting in their own self interest. In America’s free
enterprise
system, the government plays a role in attempting to prevent wild swings in economic
behavior.
Where we are in a given business cycle
affects our lives every day. If the
economy
doesn’t create enough jobs, high school
graduates have trouble finding work.
If
prices rise, but incomes don’t, our ability to
buy what we need declines.
 | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
What is
macroeconomics?
a. | The study of household
incomes | c. | The study of major
trends in the overall economy | b. | The study of corporate incomes | d. | The study of minor shifts in economic behavior of
individuals |
|
|
|
5.
|
What is
microeconomics?
a. | The study of microscopic changes in
the overall economy | c. | The study of
trends in the supply of money in circulation | b. | The study of small units of the economy, such as small
businesses | d. | The study of the banking
system |
|
|
|
6.
|
If you wanted to compare the
size of the economy in the United States and China, what economic tool would you
use.
a. | The comparative value of goods over
services in each country | c. | The amount of
economic freedom in both countries | b. | The size of their entitlement spending | d. | The GDP’s of both countries (Gross Domestic
Products) |
|
|
|
7.
|
You graduate from high school
when the business cycle is trending down. You have no intention of going to college. What effect with
the business cycle have on your life?
a. | Because business is expanding you
will most likely find a good job. | c. | You will most likely decide not to go to college because business is
bad | b. | Because business is declining you may have trouble finding a
job | d. | The business cycle has little effect on people’s
lives. |
|
|
|
8.
|
In a free market economy
individuals and businesses decide what and how much will be produced. Since individual behavior
changes over time, what effect does this have on the over-all market?
a. | Creates steady predictable behavior
on the part of consumers | c. | Creates business
cycles | b. | Causes wasteful spending | d. | Does not satisfy individual demands for goods and
services |
|
|
|
Promoting Economic Strength
Because the market is vulnerable to business cycles, the
government creates public policies that aim to stabilize the economy. Policymakers pursue three main
outcomes as they seek to stabilize the economy: high employment, steady growth, and stable
prices.
Employment
One aim of federal economic policy is to provide jobs for everyone who is able to work.
In the United States, many economists consider an unemployment rate of between 4 percent and 6
percent to be desirable. In the last half of the twentieth century, the jobless rate ranged between 3
percent and 11 percent. | Growth
Part of the American Dream has always
been for each
generation to enjoy a higher
standard of living than that of previous generations. For each
generation to do better, the economy must grow to provide additional goods and services to succeeding
generations. GDP is a measure of such growth. | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
Why does the government feel
the need to get involved in the economy in response to business cycles?
a. | To make the ups and downs of the
business cycles even more dramatic | c. | To stabilize the economy | b. | To make the economy lean toward
socialism | d. | To provide a safety net for the
poor |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which item below is
NOT one of the goals the
government pursues in order to stabilize the economy.
a. | high
employment | c. | stable
prices | b. | social safety net | d. | steady growth |
|
|
|
11.
|
What is considered a good
unemployment rate?
a. | 1% to
3% | c. | 0% to
15% | b. | 10% to 18% | d. | 4% to 6% |
|
|
|
12.
|
Your parents want you to have a
better life than they had. What must the economy do in order for that to happen?
a. | grow | c. | have no unemployment | b. | avoid business cycles | d. | make it possible for every person to go to
college |
|
|
|
Growth
Part of the American Dream has always been for each generation to enjoy a higher
standard of living than that of previous generations. For each generation to do better, the economy
must grow to provide additional goods and services to succeeding generations. GDP is a measure
of such growth.
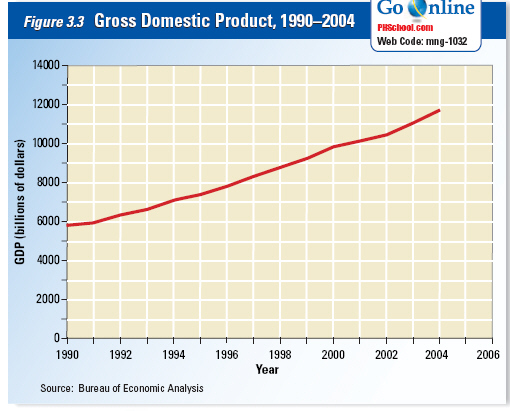
U.S. economic growth soared in the 1990s
but slowed somewhat in the 2000s.
|
|
|
13.
|
How does the growth of GDP
reflect the strengths of the free enterprise system?
a. | It shows how much the economy has
grown over time | c. | Is show the value
of the U.S. dollar over time | b. | It is a reflection of the inflation rate | d. | It is a reflection of
unemployment |
|
|
|
14.
|
What does GDP stand
for?
a. | General Department
Demographics | c. | General Deflation
Diagnosis | b. | Gross Domestic Product | d. | Gross Demand Profits |
|
|
|
15.
|
What does GDP
do?
a. | It shows how much goods, demand, and
sectors of the economy has increased over time. | c. | It measures the inflation rate as a reflection of the total health of the
economy | b. | It measures Graphically, the Demand of the
Public | d. | It measures the total output of all goods and services
produced by an economy |
|
|
|
Stability
Another macroeconomic task that the
government pursues is keeping the economy stable
and secure. Stability gives consumers, producers, and investors confidence in the economy and in our
financial institutions, promoting economic freedom and growth.
One indicator of economic
stability is general price levels. The government’s aim is to help prevent sudden, drastic
shifts in prices. A surge in overall prices puts a strain on consumers, especially people on fixed
incomes. When prices sink, producers and consumers feel the pain. A jump in the price of milk, for
example, is hard on families with children, while a plunge in milk prices hurts dairy farmers. In
either direction, major fluctuations in price levels can cause a macroeconomic chain reaction that
policymakers seek to avoid.
Another sign of economic stability is the health of the
nation’s financial institutions. None of us wants to go to the bank and
find it boarded up
and empty. When we make a bank deposit or a stock purchase, we want to know that our money will be
protected from fraud or mismanagement and shielded from the damaging effects of sudden economic
downturns.
| To provide such assurances, the federal
government monitors and regulates
American banks and other financial institutions. It produces hundreds of regulations, and it has the
power to enforce them. Federal banking regulations protect bank deposits and retirees’
pensions. Federal regulators investigate fraud and manage interest rates and the flow of money
through the economy. You’ll learn more about these functions in later
chapters.
Economic Citizenship
Achieving macroeconomic growth
and
stability is not easy. Through the way it
spends money and influences other macroeconomic
factors such as interest rates, the government helps to compensate for the typical swings of the
business cycle in our economy.
Do you expect your generation to have a higher standard of
living than that of past generations? As a voter, your elective
choices will help guide
government
economic policy. That’s why it’s more
important than ever for American
citizens
to understand the macroeconomic processes
that shape our
futures. | | |
|
|
|
16.
|
Why is it important for the
government to promote stability in the economy.
a. | So the people will not elect too
many Republicans | c. | So people,
businesses and governments will have faith in the economy. | b. | So the people will not elect too many
Democrats | d. | So the government can collect more
taxes. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Why are stable prices important
to old people and families.?
a. | Sudden decreases can place economic
hardships on people who have fixed incomes that do not increase with
inflation | c. | Stable prices mean
that people on pensions and welfare may not get a “cost of living” increase in their
pensions | b. | Sudden increases can place economic hardships on people who have fixed incomes
that do not increase with inflation | d. | Price increases are good because farmers and food manufacturers will make more
and better products available. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Why does the government make so
many banking regulations?
a. | To regulate trade help promote
American exports | c. | To protect rich
people who own the banks | b. | To increase GDP | d. | To protect deposits and prevent
fraud |
|
|
|
19.
|
It is it important
for American citizens to understand
the macroeconomic processes that shape our futures.so we can become intelligent voters and ensure a
higher standard of living
|
|
|
20.
|
What are two methods used by
the government to prevent drastic swings in the business cycle? (pick 2)
|
|
|
Technology and Productivity
The American economy maintains a far higher standard of
living, in terms of GDP, than most of the world. You’ve read that one way to preserve that high
standard is by increasing productivity—shifting the production possibilities frontier outward.
How do we do that? One way is through the American work ethic, a commitment to the value of
work and purposeful activity. Another way to increase productivity is through improved
technology.
Technological Progress
Technology is the
process used to produce a good or service. Improvements in technology
allow an economy to produce
more
output from the same or a smaller quantity
of inputs, or resources.
Technological
progress allows the United States economy
to operate more efficiently and
productively,
increasing GDP and giving U.S. businesses a
competitive advantage in the
world.
American history is full of innovations that improved productivity. Thomas
Edison’s invention of the light bulb in 1879 made possible a longer workday. From weaving looms
to tractors to computers, machines have allowed us to generate more goods in a shorter amount of time
with fewer raw materials. |
In addition, although innovation makes
some production processes and
workers out of- date, or obsolete, these resources can be
used in other ways. For example, old
industrial buildings can be converted into stores or apartments. Old machines can be recycled and
used to produce new machines.
 | | |
|
|
|
21.
|
How does technology help to
improve the economy?
a. | by improving the
environment | c. | by eliminating
business cycles | b. | by shifting the production possibilities frontier
outward | d. | by increasing savings and lowering interest
rates |
|
|
|
22.
|
Improvements in technology
a. | make geeks more attractive
| c. | make the economy more
productive | b. | takes money from the poor and gives it to the
rich | d. | make the economy more fair to the
poor |
|
|
|
23.
|
When they invented the
automobile, thousands of people who worked in the horse and carriage industry were put out of work.
How could that possibly have helped the economy?
a. | It gave the horse and carriage
people a chance to go on unemployment | c. | People who worked with horses tended to be lazy and should have been put out
of work. | b. | Fewer workers were needed in the auto
industry | d. | Eventually the horse and carriage
workers went to work in the auto industry. |
|
|
|
The
Government’s Role
Inventions are the engine of the free enterprise system. They help us to build
“more-better-faster,” thus giving consumers more economic choices. Recognizing the need
for innovation to maintain America’s technological advantage, the government provides
incentives for innovation.
Federal agencies fund scores of research and development projects
at universities. The Morrill Acts of 1862 and 1890 created so-called land-grant colleges that
received federal land and money to pursue the study of “agriculture and the mechanical
arts.” Land-grant schools from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to Texas A&M
University have been powerhouses of innovation.
The government’s own research
institutions also produce a steady stream of new technologies that make their way into the
marketplace. Probably the best-known example of such an institution is the National Aeronautics and
Space Administration (NASA). Technology created by NASA to blast humans into space and to explore
distant planets has produced amazing “spinoffs,” products with commercial uses. NASA
spinoffs include everything from a muscle stimulator for people with paralysis to a scanner that
allows firefighters to see “invisible flames” given off by alcohol or hydrogen
fires. |
The government also plays a role in innovation by offering inventors the
possibility of making huge profits in the free market. It does so by granting patents and
copyrights.
A U.S. patent gives the inventor of a new product the exclusive right to produce
and sell it for 20 years. A copyright grants an author exclusive rights to publish and sell his or
her creative works.
The Framers of the Constitution foresaw the economic need to create
incentives for innovation. Congressional authority to issue patents and copyrights is stated in
Article 1, Section 8 of the Constitution. It gives Congress the power to “promote the progress
of science and useful arts, by securing for limited times to authors and inventors the exclusive
right to their respective writings and discoveries.”
 | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
How does the government promote
inventions and technology?
a. | By providing
incentives | c. | By increasing
competiton among technology companies | b. | By insuring the technology companies always make a
profit | d. | By decreasing competition among technology
companies |
|
|
|
25.
|
What group of people was the
Morrill Acts of 1862 designed to help?
a. | teachers | c. | farmers and mechanics | b. | auto and airplane
mechanics | d. | doctors and
nurses |
|
|
|
26.
|
Television was invented by RCA
as a result of its work in radar during the war. NASA invented teflon ( the coating in frying pans)
because it needed a heat shield for the space shuttle. We call these products
a. | spin-offs | c. | unintended consequences | b. | military objectives | d. | pure science |
|
|
|
27.
|
What do patents and copyrights do?
a. | allow the government to use new
inventions | c. | ensure that taxes
will be paid on time | b. | helped the government to create new
industries | d. | protect the intellectual property of
the inventors |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which branch of the U.S.
government is given the authority to issue patents and copyrights by the Constitution?
a. | Congress | c. | Supreme Court | b. | President | d. | Commerce Department |
|
|
|
a. | microeconomics | d. | gross domestic product (GDP) | b. | business cycle | e. | macroeconomics | c. | technology | f. | induswork
ethic |
|
|
|
29.
|
the total value of all final goods and services
produced in a particular economy
|
|
|
30.
|
the process used to produce a good or
service
|
|
|
31.
|
the study of the behavior and decision making of entire
economies
|
|
|
32.
|
a commitment to the value of work and purposeful
activity
|
|
|
33.
|
a period of macroeconomic expansion followed by a
period of contraction
|
|
|
34.
|
the study of the economic behavior and decision making
of small units, such as individuals, families, and businesses
|