Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | constitution | b. | executive
power | c. | unitary government | d. | parliamentary government | e. | presidential
government | f. | legislative power |
|
|
|
1.
|
A ____ is the body of fundamental laws setting out the principles, structures,
and processes of government.
|
|
|
2.
|
A ____, often described as a centralized government, is one in which all powers
held by the government belong to a single, central agency.
|
|
|
3.
|
Under a ____, the government must resign if it receives a “vote of no
confidence.”
|
|
|
4.
|
____ is the power to make law and frame public policies.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | judicial power | b. | democracy | c. | Federal Government | d. | legislative
power | e. | confederation |
|
|
|
5.
|
The power to interpret laws, determine their meaning, and settle disputes
within a society is known as ____.
|
|
|
6.
|
Independent states that agree to form a(n) ____ may still retain their separate
identities.
|
|
|
7.
|
The structure of a(n) ____ requires that power be divided between a
state's central and local levels of government.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | Anti-Federalists | b. | boycott | c. | Commerce and Slave
Trade Compromise | d. | Connecticut Compromise | e. | English Bill of Rights | f. | Federalists | g. | Magna Carta | h. | unicameral | i. | representative government | j. | Virginia
Plan | k. | Petition of Right | l. | charter colonies | m. | Articles of
Confederation | n. | proprietary colonies |
|
|
|
8.
|
called for representation in Congress by population or by the amount of money
given to the central government
|
|
|
9.
|
idea that government should serve the will of the people
|
|
|
10.
|
agreement that, in Congress, States be represented equally in the Senate and by
population in the House
|
|
|
11.
|
those for whom the Constitution represented a too-powerful central
government
|
|
|
12.
|
first English charter of liberties which included such fundamental rights as
trial by jury and due process of law
|
|
|
13.
|
organized action to change opponents' behavior by refusing to buy or sell
their goods
|
|
|
14.
|
statement that Parliament forced the king to sign, declaring that even a
monarch must obey the law of the land
|
|
|
15.
|
organized by people to whom the king had made a grant of land available and
could be settled and governed in whatever manner they saw fit
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | State representation
proposals | b. | features of charter colonies | c. | trade regulation proposals | d. | Anti-Federalist
objections to the Constitution |
|
|
|
16.
|
objections to ratification process, importance of States' rights, concern
for God
|
|
|
17.
|
Connecticut Compromise, New Jersey Plan, Virginia Plan
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | bicameral | b. | repeal | c. | charter | d. | quorum | e. | Federalists | f. | ratification | g. | unicameral |
|
|
|
18.
|
From its one chamber, the ____ legislature of the Second Continental Congress
exercised both legislative and executive powers.
|
|
|
19.
|
The colonists organized a boycott of all trade with England, hoping to force
the ____ of restrictive laws.
|
|
|
20.
|
Some of the 13 colonies were established by ____, under a grant of authority
from the English crown.
|
|
|
21.
|
No one opposed ____ of the Constitution more vehemently than Patrick
Henry.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | amendment | b. | Bill of
Rights | c. | checks and balances | d. | constitutionalism | e. | article | f. | rule of law | g. | separation of
powers |
|
|
|
22.
|
A(n) ____ is a way to change the Constitution.
|
|
|
23.
|
The government and its officers must obey the ____, which is another way of
describing the concept of limited government.
|
|
|
24.
|
A(n) ____ is one of the seven numbered sections of the Constitution.
|
|
|
25.
|
The system of ____ helps keep one branch of government from dominating the
actions of the others.
|
|
|
26.
|
The Constitution provides for the ____ by creating three distinct branches of
government: legislative, executive, and judicial.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | checks and
balances | b. | Bill of Rights | c. | executive agreement | d. | formal
amendment | e. | judicial review | f. | unconstitutional |
|
|
|
27.
|
A(n) ____ carries the same force of law as a treaty.
|
|
|
28.
|
A governmental action that denies someone fair and equal treatment under the
law may be declared ____.
|
|
|
29.
|
The first ten amendments are called the ____.
|
|
|
30.
|
Changes to the written provisions of the Constitution may be made only through
the process of ____.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than once. a. | block grant | b. | concurrent powers | c. | exclusive
powers | d. | revenue sharing | e. | reserved powers |
|
|
|
31.
|
those powers exercised solely by the National Government
|
|
|
32.
|
federal aid given to States and local governments with virtually no conditions
attached
|
|
|
33.
|
those powers not denied to the States, and not granted specifically to the
National Government by the Constitution
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than once. a. | enabling act | b. | delegated powers | c. | division of
powers | d. | exclusive powers | e. | Privileges and Immunities
Clause |
|
|
|
34.
|
the separation of governmental powers between the National Government and the
50 State governments
|
|
|
35.
|
those powers granted in the Constitution only to the National
Government
|
|
|
36.
|
provides that a State cannot take unfair advantage in its laws of the residents
of another State
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than once. a. | act of admission | b. | extradition | c. | grants-in-aid
program | d. | inherent powers | e. | enabling act | f. | Privileges and
Immunities Clause |
|
|
|
37.
|
In order for a new State to be admitted to the Union, Congress must pass a(n)
____ after a State constitution has been approved by the people of the proposed State.
|
|
|
38.
|
States may receive grants of federal land under a(n) ____ for such purposes as
establishing schools and colleges.
|
|
|
39.
|
Congress must pass a(n) ____ before a territory can write a proposed State
constitution.
|
|
|
40.
|
According to the ____, a State cannot take unfair advantage in its laws of the
residents of another State.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than once. a. | act of admission | b. | delegated powers | c. | enabling
act | d. | reserved powers |
|
|
|
41.
|
A territory seeking Statehood is first directed to prepare a State constitution
by means of a(n) ____.
|
|
|
42.
|
The National Government has three types of ____ that have been granted to it in
the Constitution.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
43.
|
Isaiah’s father works for the government of a democracy, and he has the
power to execute, enforce, and administer the law. What type of basic powers does Isaiah’s
father handle?
a. | legislative powers | b. | executive powers | c. | confederative
powers | d. | judicial powers |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which of the following ideas was NOT promoted by the “social
contract” theory?
a. | common defense | b. | popular sovereignty | c. | limited
government | d. | individual rights |
|
|
|
45.
|
In this political cartoon, which statement best describes how the two chefs make
a democracy stew?  a. | A democracy is made of ingredients added deliberately and
precisely. | b. | A democracy cannot have competing interests. | c. | A democracy is made
by blending and adjusting competing views and interests. | d. | A democracy is made
of similar views and interests. |
|
|
|
46.
|
This map shows the three types of colonial government that were established in
1775. How did the government of Connecticut differ from the one in North Carolina? 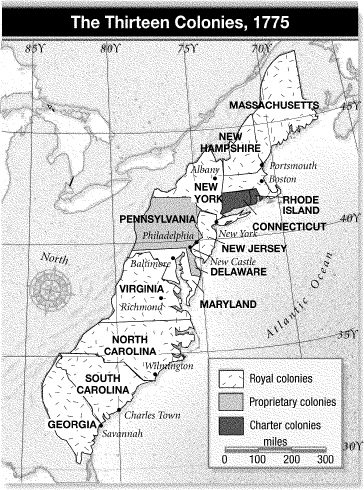 a. | In Connecticut the colony was subject to the direct control of the Crown, and in
North Carolina the colony was governed by a proprietor. | b. | In Connecticut the
colony was subject to the direct control of the governor, and in North Carolina the colony was
governed by a proprietor. | c. | In Connecticut the colony was self-governing,
and in North Carolina the colony was subject to the direct control of the Crown. | d. | In Connecticut the
colony was governed by a proprietor, and in North Carolina the colony was
self-governing. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Although the first State constitutions differed considerably, one of the most
common features was the principle of popular sovereignty. If someone were running for President on a
platform of popular sovereignty, what principle would he or she be emphasizing?
a. | separation of powers | b. | consent of citizens | c. | limited
government | d. | civil rights |
|
|
|
48.
|
Although the Articles of Confederation established a relationship among the
States, the 1780s was a critical period because it exposed weaknesses in the document. What resulted
from these weaknesses?
a. | mass migration from southern States to western territories | b. | economic and
political instability in every State | c. | unfair taxation of some citizens without
representation in Congress | d. | a banking system inadequate to fulfill every
State’s needs |
|
|
|
49.
|
What did the smaller States fear during the framing of the Constitution that led
to a series of compromise proposals?
a. | They were worried that the larger States would have the power to regulate interstate
commerce. | b. | They were worried that the larger States would have greater representation in
Congress and would dominate the government. | c. | They were worried that the smaller States would
be unable to participate in the slave trade. | d. | They were worried that the larger States would
have fewer separations of power and would use this loophole to gain control of the
Senate. |
|
|
|
50.
|
The concept known as _____ means that basic powers are distributed among three
distinct branches of government.
a. | constitutionalism | b. | separation of powers | c. | limited
government | d. | distributed government |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following is NOT a method of proposing a formal constitutional
amendment?
a. | It may be proposed by a national convention and ratified by conventions in two thirds
of the States. | b. | It may be proposed by a two-thirds vote in each house of Congress and be ratified by
three fourths of the State legislatures. | c. | It may be proposed by Congress and then
ratified by conventions in three fourths of the States. | d. | It may be proposed
by a national convention called by Congress at the request of two thirds of the State
legislatures. |
|
|
|
52.
|
In 1999, President Clinton used his executive powers to send troops to the
Yugoslav province of Kosovo. Considering that only Congress can declare war, how was President
Clinton able to send troops into combat without such a declaration?
a. | As the President of the United States, Clinton had exclusive authority over
Congress. | b. | As commander in chief, the President can declare war if conditions set forth in the
War-Peace Agreement are met. | c. | President Clinton was able to use his veto
power to overturn Congress’s decision not to send troops. | d. | As the commander in
chief, Clinton used his power to use the armed forces abroad without congressional
approval. |
|
|
|
53.
|
The Constitution delegates powers to the National Government, powers to the
States, and powers that both have. Which of the following belongs in the center area of this Venn
diagram illustrating the division of powers? 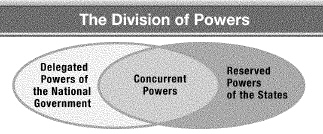 a. | borrow money | b. | regulate foreign trade | c. | coin
money | d. | establish public schools |
|
|
|
54.
|
Congress appropriated grant money to Sam’s school district to improve its
school lunch program. In exchange for the grant, three conditions had to be met: | (1) | The money had to be used for
this specific purpose. | | (2) | The State had to give the school district matching funds. | | (3) | An agency had to be established to administer
the grant. | | |
What type of grant was Sam’s school district given? a. | nutritional grant | b. | categorical grant | c. | block
grant | d. | project grant |
|
|
|
55.
|
A fugitive from justice in one State is captured in another State. According to
the laws of extradition, what will happen to this person?
a. | The fugitive will be tried in the State where he or she was
captured. | b. | The fugitive must appear before the supreme court in the State where the crime was
committed. | c. | The fugitive will be returned to the State that has jurisdiction over the
crime. | d. | The fugitive will be sent to a third, impartial State, where he or she will be
tried. |
|
|
|
56.
|
What clause of the Constitution states that no State can draw unreasonable
distinctions between its own residents and those persons who live in other States?
a. | Privileges and Immunities Clause | b. | Full Faith and Credit
Clause | c. | Interstate Compact Clause | d. | Extradition and Immunities
Clause |
|
|
|
57.
|
Which of the following served as the first national government of the United
States?
a. | First Continental Congress | b. | Albany Plan of Union | c. | Second Continental
Congress | d. | Stamp Act Congress |
|
|
|
58.
|
What does the constitutional principle of judicial review mean?
a. | People are the source of any and all government power. | b. | Government is
restricted in what it may do, and each individual has rights the government cannot take
away. | c. | The courts have the power to determine the constitutionality of a governmental
action. | d. | The powers of the three branches of government overlap to check one another’s
actions. |
|