Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | commerce power | b. | copyright | c. | indirect tax | d. | legal
tender | e. | patent |
|
|
|
1.
|
a charge levied by the government, first paid by one person, then passed on to
another
|
|
|
2.
|
the exclusive legal right to copy, sell, or publish a piece of creative
work
|
|
|
3.
|
a grant for the exclusive right to make, use, or sell new or improved
inventions
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | bankruptcy | b. | eminent
domain | c. | direct tax | d. | liberal constructionist | e. | strict
constructionist |
|
|
|
4.
|
a legal proceeding for distributing to creditors the assets of those unable to
pay their debts
|
|
|
5.
|
a charge levied by the government, to be paid only by the person on whom it
is imposed
|
|
|
6.
|
someone seeking to limit the powers of Congress to its expressed powers and
only the most vital implied powers
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | successor | b. | commerce
power | c. | deficit financing | d. | liberal constructionist | e. | Necessary and Proper
Clause | f. | strict constructionist |
|
|
|
7.
|
The implied powers are based on the ____, giving Congress the ability to carry
out its expressed powers.
|
|
|
8.
|
A(n) ____ would argue for a narrow interpretation of the powers of
Congress.
|
|
|
9.
|
The ____ authorizes Congress to regulate all commercial interactions between
the States.
|
|
|
10.
|
Under the 25th Amendment, the President nominates a(n) ____ to the vice
presidency.
|
|
|
11.
|
The Federal Government has often relied on ____ to pay for wars or social
programs.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | direct tax | b. | impeach | c. | legal tender | d. | liberal
constructionist | e. | strict constructionist | f. | indirect tax | g. | subpoena |
|
|
|
12.
|
A(n) ____ favors a broad interpretation of the Constitution, which would extend
the powers of Congress.
|
|
|
13.
|
Some country doctors once accepted livestock as payment for medical bills, but
most creditors today demand to be paid in ____.
|
|
|
14.
|
The power to ____ provides a way of bringing charges against the President for
any high crimes and misdemeanors committed while in office.
|
|
|
15.
|
A(n) ____ is a monetary sum first paid by one person and then passed on to
another.
|
|
|
16.
|
A court order for a person to appear in court or produce documents is known as
a(n) ____.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
17.
|
Supreme Court rulings have been key to broadening the scope of which expressed
power?
a. | the postal power | b. | the power to tax | c. | the commerce
power | d. | eminent domain |
|
|
|
18.
|
The powers of Congress are affected by all of the following EXCEPT what
the
a. | Constitution expressly says Congress may do. | b. | Constitution says
only the States may do. | c. | States’ constitutions say Congress may
do. | d. | Constitution is silent about. |
|
|
|
19.
|
In McCulloch v. Maryland, the Supreme Court
a. | ruled the doctrine of implied powers to be unconstitutional. | b. | upheld the doctrine
of implied powers. | c. | upheld the right of the State of Maryland to
tax a federal agency. | d. | ruled the creation of a bank by Congress to be
unconstitutional. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The level of the nation's debt
a. | is limited by the Constitution. | b. | is always limited by
Congress. | c. | is not limited by any government agency. | d. | may not exceed $10
billion. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Since 1789, the expansion of power of the National Government has been caused by
all of the following EXCEPT
a. | strict construction of the Constitution. | b. | liberal construction
of the Constitution. | c. | technological advances. | d. | economic
crises. |
|
|
|
22.
|
For what purpose does the Constitution give Congress the power to regulate
bankruptcy?
a. | to finance projects that current revenues cannot cover | b. | to establish uniform
procedures for dealing with insolvent debtors | c. | to coin money and regulate its
value | d. | to act on matters affecting the nation's
security |
|
|
|
23.
|
The Supreme Court ruling in Gibbons v. Ogden expanded the
a. | currency power by including paper money as legal tender. | b. | power to tax by
allowing a tax on incomes. | c. | commerce power to include all commercial
interactions. | d. | power over territories to include the taking of private
property. |
|
|
|
24.
|
According to the Constitution, who has the sole power to impeach the
President?
a. | The House of Representatives | b. | the Vice President | c. | the Supreme
Court | d. | State courts |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following nonlegislative powers may be exercised solely by the
Senate?
a. | the power to propose constitutional amendments | b. | the power to elect a
President if the electoral college fails to do so | c. | the power to approve or reject major
presidential appointments | d. | the power to investigate the activities of
public officials |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following is an example of the investigatory powers of
Congress?
a. | accepting a treaty made by the President | b. | the power to
regulate commerce with foreign nations | c. | the power to lay and collect
taxes | d. | gathering information useful in making legislative
decisions |
|
|
|
27.
|
All the following expressed powers belong to Congress EXCEPT
a. | the power to declare war. | b. | the power to tax exports. | c. | the power to
naturalize citizens. | d. | the power to raise an
army. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Under the Constitution, Congress has the sole power to
a. | act as the commander in chief. | b. | meet with foreign leaders. | c. | declare
war. | d. | none of the above. |
|
|
|
29.
|
All treaties must be approved by a two-thirds vote of
a. | the Senate. | b. | the House. | c. | both houses of
Congress. | d. | the Supreme Court. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following powers could Congress use to help protect American car
makers from foreign competition?
a. | the currency power | b. | the power of eminent domain | c. | the power to
borrow | d. | the power to tax |
|
|
|
31.
|
Why did the Framers include the Necessary and Proper Clause in the
Constitution?
a. | to empower Congress to pass laws needed to carry out the expressed
powers | b. | to limit congressional powers to those expressly stated in the
Constitution | c. | to define the scope of the inherent powers of Congress | d. | to set forth those
powers considered necessary to the States |
|
|
|
32.
|
All the following are implied powers of Congress EXCEPT the power to
a. | set maximum work hours. | b. | restrict arms sales. | c. | fund education
programs. | d. | censor radio and TV programs. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Who has the power to propose constitutional amendments?
a. | the President | b. | the Supreme Court | c. | Congress | d. | State courts |
|
|
|
34.
|
In order to bring charges against the President or Vice President for misconduct
in office, the House of Representatives is given
a. | executive powers. | b. | the power to impeach. | c. | the power to
convict. | d. | electoral duties. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The Commerce Clause entitles Congress to
a. | tax Minnesota's wheat exports to Russia. | b. | regulate airline
routes in New England. | c. | require Texas oil tankers to dock and pay
duties in Louisiana. | d. | give San Francisco the exclusive right to
receive cargo ships from Japan. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The implied powers doctrine, upheld in McCulloch v. Maryland,
gives Congress the power to do
a. | only what the Supreme Court authorizes it to do. | b. | only what is
absolutely necessary to carry out the expressed powers. | c. | anything reasonably
related to carrying out the expressed powers. | d. | anything it decides is in the public
interest. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Congress is given investigatory powers in order to
a. | examine matters related to its lawmaking powers. | b. | bring criminal
charges against constituents. | c. | bring criminal charges against the
President. | d. | establish a national public school system. |
|
|
|
38.
|
All of the following war powers are granted to Congress EXCEPT the power
to
a. | call forth the militia. | b. | declare war. | c. | raise and support a
navy. | d. | appoint a commander in chief. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Congress shares foreign relations power with the
a. | President. | b. | Supreme Court. | c. | States. | d. | armed forces. |
|
|
|
INTERPRETING GRAPHS AND POLITICAL CARTOONS
Use the graph and
cartoon to answer the following questions.
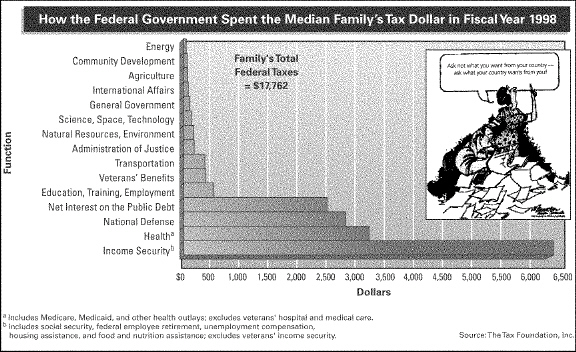
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following expenditures was greater than the expenditure on
health?
a. | net interest on the public debt | b. | income security | c. | administration of
justice | d. | international affairs |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following best expresses the main idea of the cartoon?
a. | It is selfish to expect anything from the government. | b. | The government
takes, but does not give. | c. | The government wants to meet your
needs. | d. | Paying taxes is an enjoyable experience and brings out the best in
people. |
|
|
|
42.
|
The cartoon can best be described as a call to
a. | arms. | b. | patriotism. | c. | join an interest
group. | d. | form a political party. |
|
|
|
43.
|
The graph shows that the Federal Government spent the least amount of family tax
dollars on
a. | veterans benefits. | b. | transportation. | c. | energy. | d. | income
security. |
|
|
|
44.
|
The strict constructionists agreed with the liberal constructionists in the
areas of
a. | implied powers. | b. | interstate trade. | c. | national
defense. | d. | both b and c |
|
|
|
45.
|
All of the following contributed to the growth of national power EXCEPT
a. | wars. | b. | economic crises. | c. | advances in
communication. | d. | the Bill of Rights. |
|
|
|
46.
|
In which of the following ways might the Federal Government use its taxing power
to help reverse an economic downturn?
a. | lowering the tax on exports. | b. | raising the tax on imports. | c. | raising income
taxes. | d. | laying a tax on church services. |
|
|
|
47.
|
The deficit is always _____ than the public debt.
a. | larger | b. | smaller | c. | harder to
calculate | d. | less subject to governmental limits |
|
|
|
48.
|
Based on the Supreme Court’s ruling in Gibbons v. Ogden,
1824, it would be reasonable to assume that Chief Justice John Marshall favored
a. | a strict interpretation of the Constitution. | b. | State’s
rights. | c. | a liberal interpretation of the Constitution. | d. | deficit
financing. |
|
|
|
49.
|
The Framers based their decision to deny the States the currency power on
a. | their experiences under the Articles of Confederation. | b. | the experiences of
the colonial legislatures. | c. | the social contract theory. | d. | the taxing power of
the Federal Government. |
|
|
|
50.
|
Sovereignty both _____ the States and _____ the National Government in the area
of foreign relations.
a. | empowers/empowers | b. | restricts/restricts | c. | empowers/restricts | d. | restricts/empowers |
|
|
|
51.
|
The expressed powers reflect an understanding of the importance of all of the
following to the nation EXCEPT
a. | communication. | b. | education. | c. | creative
ideas. | d. | industry. |
|
|
|
52.
|
If the caseloads of the federal courts should become too heavy, Congress has the
power to
a. | hear and try cases until the courts are caught up. | b. | create new federal
courts. | c. | transfer some cases to the executive branch. | d. | suspend the hearing
of cases until a later date. |
|
|
|
53.
|
Which of the following groups was LEAST likely to have supported the Necessary
and Proper Clause?
a. | the Framers | b. | the Supreme Court | c. | the
Federalists | d. | the Anti-Federalists |
|
|
|
54.
|
The Supreme Court could not have given “sweeping approval to the concept
of implied powers” had
a. | strict constructionists not prevented States from taxing the Second Bank of the
United States. | b. | the Supreme Court not established the power of judicial review in
1803. | c. | the Second Bank of the United States lost its charter. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
55.
|
Once the Supreme Court gave approval to the concept of implied powers,
a. | Congress was obligated to use those powers. | b. | the powers became
integral to the working of Congress. | c. | the powers could not be
revoked. | d. | Congress lost interest in the powers. |
|
|
|
56.
|
In the event that the Senate must choose a Vice President, it would take how
many votes for a candidate to win?
|
|
|
57.
|
“President Clinton was convicted of charges of perjury and obstruction of
justice in 1999.” This statement is
a. | true. | b. | false. | c. | true with regard to
the charges, but false with regard to the date. | d. | none of the
above. |
|
|
|
58.
|
The unwritten rule that can dilute the President’s appointment power
is
a. | senatorial courtesy. | b. | executive agreement. | c. | checks and
balances. | d. | party practices. |
|