Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
1.
|
The Supreme Court cases Jones v. Mayer (1968) and Runyon v.
McCrary (1976) have
a. | weakened the 13th Amendment by denying Congress the right to outlaw
discrimination. | b. | said that charges of on-the-job discrimination should be handled according to the
discretion of the individual States. | c. | strengthened the 13th Amendment by upholding
the right of Congress to outlaw discrimination against minorities. | d. | avoided dealing with
the problem of discrimination by individuals against minorities. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The right to privacy inherent in the concept of due process has been applied
with the most controversy recently in cases involving
a. | bearing arms. | b. | searches and seizures. | c. | school
attendance. | d. | abortion. |
|
|
|
3.
|
To have a fair trial, a person is guaranteed all of the following EXCEPT
a. | trial by a jury. | b. | media coverage if demanded. | c. | adequate
defense. | d. | trial within a reasonable time. |
|
|
|
4.
|
According to the Supreme Court, capital punishment
a. | is most fairly applied through use of a two-stage trial. | b. | is
unconstitutional. | c. | is cruel and unusual
punishment. | d. | can be a mandatory penalty for certain crimes. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The writ of habeas corpus is intended to prevent
a. | the accused from being unjustly arrested and imprisoned without
cause. | b. | a prisoner from being tried for the same crime twice. | c. | defendants from
being denied a lawyer. | d. | the accused from being brought before a
judge. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The main purpose of the exclusionary rule is to
a. | prevent people who are clearly guilty from going free. | b. | deter police
misconduct. | c. | allow certain kinds of "tainted" evidence to be used in
court. | d. | allow for honest mistakes by police officers. |
|
|
|
7.
|
A(n) _____, requires the police to bring a prisoner before the court and explain
why he or she should not be released.
a. | writ of habeas corpus | b. | indictment | c. | ex post facto
law | d. | bill of attainder |
|
|
|
8.
|
The most important difference between procedural and substantive due process is
that
a. | procedural due process deals with governmental methods and how they are used, whereas
substantive due process deals with the fairness of laws. | b. | the Supreme Court
can rule on cases involving procedural due process but the States rule on cases of substantive due
process. | c. | substantive due process was recognized first by the Supreme
Court. | d. | only procedural due process is covered under the 14th Amendment Due Process
Clause. |
|
|
|
9.
|
The main reason that there is no exact definition of the due process guarantees
is that the
a. | courts do not want to give away too much specific information to potential
lawbreakers. | b. | Constitution is too specific. | c. | guarantees protect citizens against unfair
processes, but not unfair laws. | d. | Supreme Court only defines the guarantees on a
case-by-case basis. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Under the 2nd Amendment,
a. | the States cannot limit a person's right to own a gun. | b. | there is no
limitation on the free flow of guns within the United States. | c. | no citizen may own a
gun. | d. | each State has the right to have a militia. |
|
|
|
11.
|
In Furman v. Georgia, 1972, the Court ruled that
a. | putting two prisoners in a cell built for one is considered cruel and unusual
punishment. | b. | the death penalty is "cruel and unusual punishment." | c. | existing death
penalty laws were unconstitutional because they gave too much discretion to judges and
juries. | d. | States can impose the death penalty for the sale of
narcotics. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The States' police power is defined as the right to
a. | allow its citizenry to keep and bear arms. | b. | keep a militia and
an armed law enforcement agency. | c. | punish those who commit crimes against the
citizenry. | d. | protect public health, safety, morals, and the general
welfare. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The 13th Amendment forbids
a. | the draft. | b. | any form of military
service. | c. | slavery and most forms of involuntary servitude. | d. | all of the
above. |
|
|
|
14.
|
A grand jury
a. | returns a true bill of indictment when it finds enough evidence to warrant a
trial. | b. | conducts its proceedings in public. | c. | plays a role in all federal and most State
criminal cases today. | d. | decides the guilt or innocence of those accused
of crimes. |
|
|
|
15.
|
When arresting a person, police must
a. | seize the person in a public place. | b. | have probable cause to believe the person is
involved in criminal activity. | c. | refrain from searching for destructible
evidence. | d. | always have a warrant in order to search for a
weapon. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The guarantee against double jeopardy protects a person from being tried
a. | for a federal crime in a State court. | b. | for more than one crime committed at any one
time. | c. | twice for the same crime. | d. | for a crime the person did not
commit. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following statements about the 4th Amendment is TRUE?
a. | It applies only to the States. | b. | It has been of little importance in our
history. | c. | It prohibits all arrests made without a warrant. | d. | It forbids
unreasonable searches and seizures. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following was declared by the Supreme Court to be "cruel and
unusual punishment"?
a. | use of the electric chair as a form of execution | b. | denying inmates
needed medical treatment | c. | use of the firing squad as a form of
execution | d. | placing two inmates in a cell built for one |
|
|
|
19.
|
The 6th Amendment's guarantee of a speedy and public trial is aimed
at
a. | eliminating overcrowded dockets in the nation's criminal
courts. | b. | trying those accused of crimes without undue delay and avoiding secret
trials. | c. | preventing jurors from being unduly influenced by public opinion. | d. | deterring potential
criminals by fear of swift and certain punishment. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The inclusion of two due process clauses in the Constitution reflects the fact
that
a. | the Constitution is written poorly in regards to due process. | b. | due process is very
easy to define. | c. | due process has two quite different meanings. | d. | the Bill of Rights
is for the National Government, and the 14th Amendment is for the States and their local
governments. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The main reason the Constitution dealt specifically with the crime of treason
was that
a. | treason was not considered a serious crime before the Constitution was
written. | b. | the Framers knew the charge of treason can be used for political
reasons. | c. | treason is a crime against the country, not against individuals. | d. | the Framers wanted
to prevent all treason in order to protect the democracy. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Because the Supreme Court has never found the 2nd Amendment to be within the
meaning of the 14th Amendment's Due Process clause,
a. | citizens are strictly forbidden to keep guns in their homes. | b. | citizens are free to
keep arms in their home without government restrictions. | c. | States can limit the
right to keep and bear arms. | d. | States may not keep
militias. |
|
|
|
23.
|
For an arrest to be lawful, police must have either a warrant or
a. | probable cause. | b. | a grand jury indictment. | c. | a bill of
attainder. | d. | a writ of habeas corpus. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The only crime that is specifically defined in the Constitution is
a. | treason. | b. | sabotage. | c. | espionage. | d. | forceful government
overthrow. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following requires a warrant?
a. | search of a vehicle if there is probable cause to believe a crime has been
committed | b. | mandatory drug-testing of student athletes. | c. | seizure of evidence
that is in plain view | d. | the installation of a
wiretap. |
|
|
|
INTERPRETING CHARTS
Use the chart to answer the following
questions.
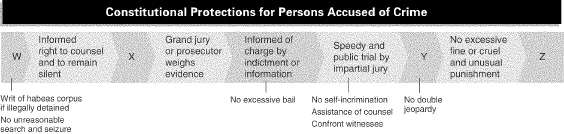
|
|
|
26.
|
Which label should appear in the box marked X?
a. | No third degree or coerced confession | b. | Right to appeal | c. | Verdict of
jury | d. | No excessive bail |
|
|
|
27.
|
In the chart, what label should appear in the box marked W?
a. | Arrest on warrant or probable cause | b. | No third degree or coerced
confession | c. | Verdict of jury | d. | Right to appeal |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which label should appear in the box marked Y?
a. | Arrest on warrant or probable cause | b. | No third degree or coerced
confession | c. | Verdict of jury | d. | Right to appeal |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which label should appear in the box marked Z?
a. | Right to appeal | b. | No third degree or coerced
confessions | c. | Arrest on warrant or probable cause | d. | Verdict of jury |
|
|
|
30.
|
The fifth box lists two ways the accused can be informed of charges. What is a
third way?
a. | writ of habeas corpus | b. | presentment | c. | bill of
attainder | d. | Supreme Court ruling |
|
|
|
31.
|
Who is present at the 4th step?
a. | the jury | b. | the prosecution | c. | both the prosecution
and the defense | d. | the defense |
|
|
|
32.
|
The long series of Court rulings on the rights of the accused have established
that
a. | society is best protected when the rights of the accused are
protected. | b. | every accused person is presumed innocent until proven guilty. | c. | if police do not
follow the letter of the law, their conduct may result in a guilty person going
free. | d. | all of the above. |
|
|
|
33.
|
The writ of habeas corpus can be suspended during war because in that
case
a. | court officers will be unavailable to appear in court. | b. | the entire
Constitution has been suspended. | c. | the President assumes the powers of all three
branches of government. | d. | the public good outweighs individual civil
liberties. |
|
|
|
34.
|
In the guidelines established by the Court in Roe v. Wade, which
of the following are considered?
a. | the rights of the mother | b. | the rights of the unborn
child | c. | both a and b | d. | neither a nor b |
|
|
|
35.
|
One thing the Civil War proved was that
a. | a distinction would have to made between slavery and involuntary
servitude. | b. | the Federal Government had to take control of prohibiting slavery, rather than leave
that decision to the States. | c. | racial discrimination led to
slavery. | d. | thereafter, the draft would have to be considered “involuntary
servitude.” |
|
|
|
36.
|
The guarantees of due process place the burden for meeting these guarantees
on
a. | lawmakers. | b. | the police. | c. | both lawmakers and
those who execute the laws. | d. | those who execute the
laws. |
|
|
|
37.
|
The 4th Amendment is particularly aimed at
a. | protecting an individual’s right to keep and bear arms. | b. | “movable
scenes of crime” such as automobiles or boats. | c. | preventing the police from abusing their
power. | d. | preventing the use of the exclusionary rule. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The idea that the 13th Amendment applies to the actions of government and
of private individuals
a. | was clear since the amendment was ratified in 1865. | b. | was not thought to
be the case until more than 100 years after the amendment was ratified. | c. | has been struck down
by the Supreme Court in a series of cases dating from the early 1900s. | d. | was not clarified
until after the passage of the 14th Amendment. |
|
|
|
39.
|
The central issue in the conflict between the police power and individual rights
is whether
a. | individual rights under the 14th Amendment are violated when a State exercises its
police power. | b. | the States or the Federal Government should exercise the police
power. | c. | the police power is constitutional. | d. | an individual can exercise the police
power. |
|
|
|
40.
|
The moratorium placed on the death penalty in Illinois by Governor George Ryan
was of particular note because
a. | two of every three Americans support the death penalty. | b. | Governor Ryan had
been a “longtime supporter of capital punishment.” | c. | Furman v.
Georgia had already struck down the Illinois law. | d. | both b and
c |
|
|
|
41.
|
The right to keep and bear arms set out in the 2nd Amendment applies
a. | only to the Federal Government. | b. | only to the States. | c. | to the National
Firearms Act of 1934. | d. | to both the States and the Federal
Government. |
|
|
|
42.
|
One assumption underlying the establishment of the death penalty as the maximum
penalty for treason against the United States is that
a. | only the Federal Government, not the States, can charge a person with
treason. | b. | the crime of treason can jeopardize the nation’s very
existence. | c. | tyrants have been known to use charges of treason to eliminate their
opponents. | d. | treason is the only crime defined in the
Constitution. |
|
|
|
43.
|
The 6th Amendment right to a public trial is meant to safeguard the rights of
the
a. | public. | b. | defendant. | c. | media. | d. | party filing criminal charges against the
defendant. |
|
|
|
44.
|
The issue that tips the scales away from bail toward preventive detention is
whether
a. | the defendant is likely to commit a crime before trial. | b. | a defendant needs to
prepare for his or her trial. | c. | a person is presumed innocent until proven
guilty. | d. | all of the above. |
|
|
|
45.
|
None of the following involve double jeopardy EXCEPT
a. | trying a case a second time in a higher court when the verdict has been
appealed. | b. | trying a person for more than one crime committed during a single
act. | c. | trying a person for the same crime in both the federal and the State
courts. | d. | trying a person for the same crime when a jury has already declared that person
innocent. |
|
Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | bill of
attainder | b. | capital punishment | c. | probable cause | d. | bench
trial | e. | exclusionary rule | f. | double jeopardy |
|
|
|
46.
|
Current polls indicate that two of every three Americans support ____ for those
convicted of murder.
|
|
|
47.
|
The defendant had a(n) ____ with only a judge deciding the case.
|
|
|
48.
|
The ____ says that evidence gained as a result of an illegal act by police
cannot be used against the person from whom it was seized.
|
|
|
49.
|
The prohibition of ____ prevents a person from being tried twice for the same
crime.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | police power | b. | probable
cause | c. | bill of attainder | d. | double jeopardy | e. | Miranda
Rule | f. | indictment |
|
|
|
50.
|
A(n) ____ is a formal complaint that the prosecutor lays before a grand
jury.
|
|
|
51.
|
Neither Congress nor the States can pass a(n) ____ that inflicts punishment
without a court trial.
|
|
|
52.
|
The ____ begins with these words: "You have the right to remain
silent."
|
|
|
53.
|
In order to obtain a warrant, police must have ____.
|