Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
The Major Principles of Government
Embodied in the Constitution
Major Ideas of American Government are in the Constitution The governmental
framework supplied by the Constitution has a number of elements. In general, they fall under six
broad principles. Much of the Constitution seems to focus on how the government should be
controlled. As James Madison (1751-1836) once said, after you have given the government the ability
to control its citizens, you have to "oblige it to control itself." In keeping with the
concept of controlling the government, the first basic governing principle of the Constitution is
limited government. Governments that are not limited are dictatorships. Here are the six
broad principles:
1. limited government
2. popular sovereignty,
3. separation of
powers,
4. checks and balances,
5. judicial review, and
6.
federalism.
What do they
mean?????
| |
|
|
|
1.
|
According to the passage above,
a good part of the Constitution is devoted to
a. | making the government
stronger | c. | making the
government weaker | b. | controlling the government to limit its
power | d. | making the government more powerful so it can protect its
citizens |
|
|
|
2.
|
From the passage above we can
infer that James Madison
a. | hated the
government | c. | trusted the
government | b. | distrusted the government | d. | did not like citizens |
|
|
|
Limited
Government
The framers were
fearful of the powerful English monarchy, against which they had so recently rebelled. They therefore
included in the Constitution the principle of limited government, which means that the national
government created by the Constitution can do only what the people allow it to do. This principle can
be found in many parts of the Constitution. For example, while Articles I, 11, and III indicate what
the national government can do, the first nine amendments to the Constitution list ways that the
national government cannot limit certain individual freedoms. Under a limited government, all
citizens must live according to the rule of law. Like other citizens, those who run the government
must always obey the laws found in the Constitution. Otherwise stated, no person- even the
president-is above the law.
| |
|
|
|
3.
|
In a limited form of
government
a. | only the president is above the
law | c. | everyone except the president is
above the law | b. | even the president is above the law | d. | no one is above the law |
|
|
|
4.
|
What is the main idea of the
passage above?
a. | The Constitution is designed to
limit the power of government | c. | Only the president is above the law | b. | The constitution is designed to enhance the power of
government | d. | No one makes the laws for the U.S.
except the Congress. |
|
|
|
Popular
Sovereignty
Popular
sovereignty means that the people are the ultimate source of any power given to the government.
Remember that the phrases that frame the Preamble to the Constitution are "We the People of the
United States ... do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America."
In other words, it is the people who form the government. The principle of popular sovereignty is
closely linked to the principle of limited government. According to both principles, the people are
the ultimate source of governmental authority.
| |
|
|
|
5.
|
Popular sovereignty
means
a. | being sovereign is
popular | c. | it is important to
be popular | b. | the people are more powerful than the
government | d. | you muse be free to be
popular |
|
|
|
6.
|
Who established the
Constitution the United States?
a. | George
Washington | c. | the
people | b. | James Madison | d. | the government |
|
|
|
Separation of
Powers
The framers of the
Constitution wanted to create a government that would prevent the rise of tyranny, absolute and
unlimited power and authority. To do so, they separated the powers of the government. They
distributed governmental powers among three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. When
powers are separated in this way, no one branch has enough power to dominate the others. The plan
for separation of powers used in the Constitution is called the Madisonian Model, for James
Madison, who developed it. The plan is laid out in Articles 1, 11, and 111. Congress, or the
legislative branch, passes laws; the president, or the executive branch, carries them out; and the
courts, or the judicial branch, interpret them.
| |
|
|
|
7.
|
Why did James Madison believe
it was important to separate the government into branches?
a. | He thought it would make the
government more stable and secure | c. | He wanted to keep each branch from becoming too
powrful | b. | He did not like the Senate and wanted to limit it’s
power. | d. | He did not trust
people |
|
|
|
8.
|
In the Madisonian model of
government, each branch of the government was equal and has the same
responsibilities.
|
|
|
9.
|
How many branches of government
does the Constitution create?
|
|
|
Checks and
Balances
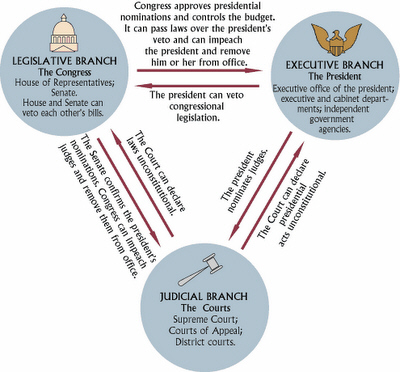
The separation of powers is part of a system of checks and
balances. The framers feared that one branch of government could dominate the other two. In order to
prevent this, the framers made sure that each branch of government could exercise certain powers over
the actions of the other branches. The president checks Congress by holding veto power, which is the
ability to refuse to sign congressional bills into law. Congress, in turn, controls taxes and
spending, and the Senate must approve presidential appointments. For example, the president can
appoint justices to the Supreme Court, but only with the approval of the Senate. Under the system of
checks and balances, each branch's independence is protected. At the same time, however,
the system calls for cooperation, because in order to take an action, at least two branches must work
together. For example, Congress can pass a law, but the executive branch must approve, administer,
and enforce it. Thus, the branches depend on each other, but they also maintain their
independence.
| |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the purpose of
checks and balances in
the U.S. government?
a. | make sure each branch has the same
power | c. | cut down on excessive
regulation | b. | balances help the government to run smoother | d. | prevent any one branch of government from becoming too
powerful |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which branch of government has
the power to veto laws written by Congress?
a. | executive | c. | judicial | b. | legislative | d. | Supreme Court |
|
|
|
12.
|
The president appoints Mr.
Schneemann to be the Ambassador to Mexico. Which branch of government must approve the
nomination?
a. | executive | c. | congress | b. | judicial | d. | courts |
|
|
|
13.
|
The system of checks and
balances in the U.S. government keep the branches from working together
|
|
|
Judicial
Review
Judicial review
refers to the power of the courts to decide whether a law or other governmental action violates the
Constitution. In cases that come before the U.S. Supreme Court, if the justices find that a
federal or state law violates the U.S. Constitution, that law is declared unconstitutional. Such a
law no longer has any validity or legitimacy-it is as if it did not exist. For example, suppose your
state passed a law that allowed the state police to monitor telephone conversations (called
wiretapping) without formally obtaining permission from a judge. The U.S. Supreme Court might strike
down that law as unconstitutional because it violates the Fourth Amendment to the Constitution.
The Constitution does not specifically mention judicial review. Most constitutional scholars
believe, however, that the framers meant the federal courts to have that power. For example, in
Federalist Paper No. 78, Alexander Hamilton made the following statement: The interpretation of the
laws is the proper and peculiar province [specialty] of the courts. A constitution is, in
fact, and must be regarded by the judges, as a fundamental law. It therefore belongs to them to
ascertain its meaning, as well as the meaning of any particular act proceeding from the legislative
body. If there should happen to be an irreconcilable variance between the two, . . . the Constitution
ought to be preferred to the statute Judicial review became part of the U.S. system in the 1803 case
of Marbury v. Madison. In this famous case, the Supreme Court ruled for the first time that
part of an act passed by Congress was unconstitutional. Chief Justice John Marshall declared that it
is "the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is." You can read
about this case in Case Study: Government in Action-Marbury v. Madison (1803). After this
important decision, the Supreme Court became part of the checks and balances system. Through the
power of judicial review, the Court could declare actions of the other two branches of government
unconstitutional.
| |
|
|
|
14.
|
The case of Marbury v. Madison
a. | said the laws passed by the
executive branch might be unconstitutional | c. | made the judicial branch of government more p;powerful than the
others | b. | made the legislative branch of government more powerful than the
others | d. | established the power of the Supreme Court to review the
actions of the other branches |
|
|
|
15.
|
What happens to laws that
violate the constitution?
a. | the Courts declares them
unconstitutional | c. | the Congress
refuses to enforce them | b. | the president declares them to be
unconstitutional | d. | the judicial branch must re-write
them |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the purpose of
judicial
review?
a. | helps the government to enforce the
law | c. | gives the President a chance to
review and re-write the laws that are unconstitutional | b. | keeps the government from violating the
Constitution | d. | gives the courts a chance to review
and re-write the laws that are unconstitutional |
|
|
|
Federalism
The Constitution set up a form of government based on
the principle of federalism. In a federal system, some powers belong to the national, or federal,
government, while others belong to the states. This division of powers was a compromise between
two groups of delegates to the Philadelphia convention: those who had strong nationalist views and
those who felt that the states should retain most of their rights. In the next chapter, you will read
about the federal system in more detail.
| |
|
|
|
17.
|
The system of federalism
a. | makes sure the states do not have
power | c. | gives some power to the U.S.
government and some power to the states. | b. | makes sure the U.S. government does not have
power | d. | ensures that all laws are
constitutional |
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | judicial
review | e. | checks and
balances | b. | popular sovereignty | f. | veto | c. | unconstitutional | g. | Marbury v. Madison | d. | federalism | h. | preamble |
|
|
|
18.
|
established the power to the
Supreme Court to review laws
|
|
|
19.
|
says that government power is
shared between the U.S. government and the states.
|
|
|
20.
|
strategy for keeping any one
branch of government from becoming too powerful
|
|
|
21.
|
the ability of the courts to
rule a law unconstitutional
|
|
|
22.
|
the president refuses to sign
a law that he does not agree with
|
|
|
23.
|
a law that violates the
Constitution
|
|
|
24.
|
the introduction to the
Constitution that sets forth the purpose of government
|
|
|
25.
|
the idea that all power
resides with the people of the United States
|