Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | Anti-Federalists | b. | boycott | c. | Commerce and Slave
Trade Compromise | d. | Connecticut Compromise | e. | English Bill of Rights | f. | Federalists | g. | Magna Carta | h. | unicameral | i. | representative government | j. | Virginia
Plan | k. | Petition of Right | l. | charter colonies | m. | Articles of
Confederation | n. | proprietary colonies |
|
|
|
1.
|
called for representation in Congress by population or by the amount of money
given to the central government
|
|
|
2.
|
idea that government should serve the will of the people
|
|
|
3.
|
agreement that, in Congress, States be represented equally in the Senate and by
population in the House
|
|
|
4.
|
those for whom the Constitution represented a too-powerful central
government
|
|
|
5.
|
first English charter of liberties which included such fundamental rights as
trial by jury and due process of law
|
|
|
6.
|
organized action to change opponents' behavior by refusing to buy or sell
their goods
|
|
|
7.
|
statement that Parliament forced the king to sign, declaring that even a
monarch must obey the law of the land
|
|
|
8.
|
organized by people to whom the king had made a grant of land available and
could be settled and governed in whatever manner they saw fit
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | State representation
proposals | b. | features of charter colonies | c. | trade regulation proposals | d. | Anti-Federalist
objections to the Constitution |
|
|
|
9.
|
objections to ratification process, importance of States' rights, concern
for God
|
|
|
10.
|
Connecticut Compromise, New Jersey Plan, Virginia Plan
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | bicameral | b. | repeal | c. | charter | d. | quorum | e. | Federalists | f. | ratification | g. | unicameral |
|
|
|
11.
|
From its one chamber, the ____ legislature of the Second Continental Congress
exercised both legislative and executive powers.
|
|
|
12.
|
The colonists organized a boycott of all trade with England, hoping to force
the ____ of restrictive laws.
|
|
|
13.
|
Some of the 13 colonies were established by ____, under a grant of authority
from the English crown.
|
|
|
14.
|
No one opposed ____ of the Constitution more vehemently than Patrick
Henry.
|
|
|
INTERPRETING CHARTSThe events leading up to the American
Revolution and Constitutional Convention can be seen as a series of causes and effects. Complete the
chart below by filling in each box with the letter of the correct term from the list on the right.
The first one is done for you. You will not use all the terms.
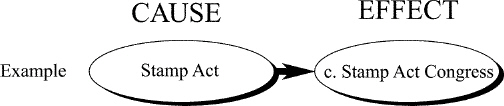 a. | Intolerable Acts | b. | need for strong central
government | c. | Stamp Act Congress | d. | creation of army, money system,
treaties |
|
|
|
15.
|
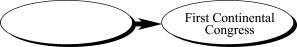
|
|
|
16.
|
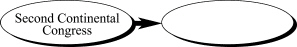
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
17.
|
In the charter colonies, most governmental matters were handled by
a. | the British monarch. | b. | Parliament. | c. | a
proprietor. | d. | the colonists. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which idea is NOT included in the Declaration of Independence?
a. | People have certain natural rights. | b. | God gives certain people the right to
govern. | c. | Government can exist only with the people's permission. | d. | The people may
change or abolish the government. |
|
|
|
19.
|
All of the following influenced the Framers in developing the Constitution
EXCEPT
a. | State constitutions. | b. | John Locke's Two Treatises of
Government. | c. | Virginia's royal charter. | d. | British
tradition. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which colony was founded mainly as a place for personal and religious
freedom?
a. | Virginia | b. | Georgia | c. | Massachusetts | d. | New York |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which feature did the State constitutions and the Articles of Confederation have
in common?
a. | royal governors | b. | bill of rights | c. | principle of popular
sovereignty | d. | a strong executive elected by popular vote |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of these State constitutions is the oldest and still in force
today?
a. | Massachusetts | b. | South Carolina | c. | New
Hampshire | d. | Virginia |
|
|
|
23.
|
After the Revolutionary War, the National Government
a. | proved too weak to deal with growing economic and political
problems. | b. | refused to repay the war debt it owed to the States. | c. | permitted the States
to make agreements with foreign governments. | d. | began imposing harsh tax policies on property
owners and merchants. |
|
|
|
24.
|
In Benjamin Franklin's opinion, the final Constitution created by the
delegates can best be summarized as
a. | absolutely perfect. | b. | as near perfect as
possible. | c. | showing errors of opinion and self-interest. | d. | as full of
imperfections as those who assembled it. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following statements about the inauguration of George Washington as
the first U.S. president is NOT true?
a. | It followed his unanimous election in the Electoral College. | b. | It took place in New
York City, the country's temporary capital. | c. | It came after the ratification of the
Constitution. | d. | It followed Washington's appointment of James Madison as the first Vice
President. |
|
|
|
26.
|
A major objective of both the Annapolis Convention and the Philadelphia
Convention was to
a. | determine how the States should be represented in Congress. | b. | recommend a federal
plan for regulating interstate trade. | c. | raise an army for quelling incidents like
Shay's Rebellion. | d. | limit the growing power of the National
Government. |
|
|
|
27.
|
The government set up by the Articles of Confederation had
a. | no legislative or judicial branch. | b. | only a legislative and an executive
branch. | c. | only a legislative branch, consisting of a unicameral Congress. | d. | only a legislative
branch, consisting of a bicameral Congress. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which was an achievement of the Second Continental Congress?
a. | preparing a Declaration of Rights | b. | raising an American army | c. | establishing a
strong central government | d. | passing the Intolerable
Acts |
|
|
|
29.
|
Parliament first limited the power of the Crown under the
a. | Intolerable Acts. | b. | Petition of Right. | c. | Stamp Act of
1765. | d. | English Bill of Rights. |
|
|
|
30.
|
The Federalist was written to
a. | win support for the Constitution in New York. | b. | expose the lack of
civil liberties protected in the Constitution. | c. | urge ratification of the Constitution in
Virginia. | d. | condemn the Constitution for the absence of any mention of
God. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following directly influenced the Framers in the development of the
Constitution?
a. | Chinese tradition | b. | the Articles of
Confederation | c. | Spanish tradition | d. | Virginia's royal
charter |
|
|
|
32.
|
At the Philadelphia Convention, the delegates agreed to
a. | make minor revisions to the Articles of Confederation. | b. | open their sessions
to the public. | c. | pass proposals by unanimous vote only. | d. | draft a new
constitution. |
|
|
|
33.
|
By the mid-1700s, British rule in the colonies was marked by
a. | allowing a certain degree of self-rule to the colonists. | b. | imposing harsh and
restrictive trade practices. | c. | passing increasingly high
taxes. | d. | forcing the colonies to attack other colonial powers. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Delegates met at Mount Vernon and Annapolis to
a. | recommend a federal plan for regulating commerce. | b. | recommend a way to
start a national army. | c. | recommend ways to end
slavery. | d. | attend a social gathering in honor of George
Washington. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The first State constitutions, adopted after independence,
a. | placed most authority with the State governors. | b. | provided for lengthy
terms for elective offices. | c. | placed most authority with the State
legislatures. | d. | extended voting rights to all adult State residents. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The Second Continental Congress was similar to the first in the
a. | composition of its members. | b. | creation of a monetary
system. | c. | borrowing of money. | d. | raising of an
army. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Much of the Declaration of Independence consists of
a. | statements of the desire to separate from England. | b. | lists of the rights
of all people. | c. | complaints of the wrongs done to the colonists. | d. | threats of revenge
for English mistreatment. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Benjamin Franklin's attitude toward the new constitution may be summarized
as a combination of
a. | despair and hope. | b. | astonishment and optimism. | c. | relief and
anger. | d. | fatigue and thankfulness. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which best describes the event leading to the inauguration of the first
President of the United States of America?
a. | The people elected the President and Vice President. | b. | The people elected
the President and electors selected the Vice President. | c. | The States selected
electors who voted to elect the President and Vice President. | d. | Congress elected the
President and Vice President. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Much of the work of the Framers centered around the proposals that had been set
out in
a. | the Virginia Plan. | b. | the New Jersey Plan. | c. | The
Federalist. | d. | the Declaration of Independence. |
|
|
|
41.
|
The success of which plan led to the Constitutional Convention of 1787?
a. | Albany Plan of Union | b. | Second Continental Congress's "plan
of confederation" | c. | interstate plan for regulating trade between
Virginia and Maryland | d. | compromise reached between the Virginia and New
Jersey plans |
|
|
|
42.
|
The idea that the people have the right to abolish an abusive and unresponsive
government was FIRST formally expressed by Americans in the
a. | Constitution. | b. | Petition of Right. | c. | Declaration of
Rights. | d. | Declaration of Independence. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following basic concepts of government did the Magna Carta
reflect?
a. | worth of the individual | b. | limited government | c. | ordered
government | d. | representative government |
|
|
|
44.
|
What characteristic of a state did the English colonies NOT possess?
a. | territory | b. | population | c. | sovereignty | d. | government |
|
|
|
45.
|
One major difference between the royal and proprietary colonies, on the one
hand, and the charter colonies, on the other, was that
a. | in the charter colonies, the governor was appointed, not elected. | b. | in the royal and
proprietary colonies, the legislature was unicameral. | c. | only the charter colonies were governed under a
charter granted by the king. | d. | in the charter colonies, the governor was
elected, not appointed. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which of the following BEST describes the changes in British colonial policies
in the later 1700s?
a. | The policies became more relaxed. | b. | The policies became
stricter. | c. | The policies became more inclusive. | d. | The policies became more
cooperative. |
|
|
|
47.
|
From the formation of the New England Confederation to that of the Second
Continental Congress, the colonists became progressively
a. | better organized. | b. | more defiant. | c. | both a and
b | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
48.
|
The first State constitutions focused mainly on
a. | outlining the causes of the Revolution. | b. | limiting
governmental power. | c. | establishing a unitary system of
government. | d. | abolishing restrictions on the legislature. |
|
|
|
49.
|
The powers granted to the central government under the Second Continental
Congress compared with those granted under the Articles of Confederation were
a. | dramatically different. | b. | much weaker. | c. | basically the
same. | d. | none of the above. |
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the following can be said to have contributed the MOST toward the
realization that the nation needed a stronger central government?
a. | political issues | b. | economic issues | c. | military
issues | d. | social issues |
|
|
|
51.
|
The relationship among the States during the Critical Period can be BEST
compared to
a. | a choir singing in unison. | b. | a traffic jam. | c. | children squabbling
at a playground. | d. | a baseball team at the
playoffs. |
|
|
|
52.
|
During the Critical Period, the States taxed one another’s goods and
banned some trade. Later, during the Constitutional Convention, this economic chaos led to
a. | the Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise. | b. | the Three-Fifths
Compromise. | c. | the Connecticut Compromise. | d. | none of the
above. |
|
|
|
53.
|
When crafting the new Constitution, the Framers drew from their experiences with
which of the following?
a. | the governments of ancient Greece and Rome | b. | the writings of
Rousseau and Locke | c. | their own State governments | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
54.
|
Both the Connecticut Compromise and the Three-Fifths Compromise were crucial to
the small States because
a. | they aided the economy of the small States. | b. | without them, the
small States would have had too much responsibility in the new government. | c. | they convinced James
Madison to support the small States. | d. | without them, the small States would have
carried little weight in the new government. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Why was it ironic that Virginia was one of the last States to ratify the
Constitution?
a. | It was one of the largest States. | b. | The new government could not succeed without
Virginia’s support. | c. | Virginia’s leading voices supported a
strong central government. | d. | Virginia delegate James Madison contributed
more to the document than any other delegate. |
|
|
|
56.
|
The objections of the Anti-Federalists can be BEST summed up as:
a. | a fear that the small States would not have a say in the new
government | b. | a fear that the new government would be too weak to succeed | c. | a fear that the new
government would have too much power and the people, too little power | d. | a fear that too few
people had participated in the writing of the Constitution |
|
|
|
57.
|
The Federalist can be called a “campaign document” because
it
a. | was written to draw people’s attention to the need to defeat the
British. | b. | contained the best political writings in the English language. | c. | was written to
convince voters to support the new Constitution. | d. | was written by an anonymous
author. |
|