|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
Study the introduction to this unit above. What are you expected to learn from
this unit? Enter your answer on the right.
Also, study the vocabulary words and look for them as
you work your way through this unit.
Good luck.
|
|
|
You cannot find today any economic
system that
relies exclusively on central
planning or the individual initiative of the
free market.
Instead, most economies are a
mixture of economic systems. Most
contemporary mixed economies
blend the
market with government intervention, or
involvement, in the marketplace.
| The Rise of Mixed
Economies
No single economic system has all the
answers. Centrally planned economies
are
cumbersome, do not adequately meet
consumer needs, and limit freedom.
Traditional
economies have little potential
for growth or change. Even market
economies, with all their
advantages, have
certain drawbacks. | | |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which statement below is true?
a. | Most economies today are free market economic systems | c. | Most economies today are centrally
planned systems | b. | Most economies today are free market with some government
intervention | d. | Traditional
economies are the most successful economic systems in the world today |
|
|
|
3.
|
What is the main drawback of traditional economies?
a. | They change too easily therefore people do not have confidence in them | c. | They are reluctant
to change so they are unable to keep up with social changes | b. | They are
undemocratic | d. | The people who
participate in traditional economies are usually uneducated |
|
|
|
The Limits of Laissez Faire
Adam Smith and
other early free market
philosophers believed that, left to its own
devices, the free market
system would
provide the greatest benefit for consumers
and raise the standard of living. They
preached laissez faire, the doctrine that
government generally should not intervene
in
the marketplace. (See the Profile of
Adam Smith on page 33.) Even Smith
acknowledged, however,
the need for a
certain limited degree of government intervention in the economy.
As market
economies have evolved since
Smith’s time, government intervention has
become greater
because some needs and
wants of modern society are difficult to
answer in the marketplace. How
well, for
example, could the marketplace provide
for national defense or for roads
and
highway systems?
Some needs that markets could meet fall
to governments so that all
members of
society can participate. Education is one
example. Other needs that could fall
into
this category are health care and mass
transit.
The
Nine Most Terrifying Words:
“I’m from the
government and I’m here to help.”
Ronald Reagan
| Governments create laws protecting
property rights and
enforcing contracts.
There would be little incentive to develop
new products without property
rights or
patent laws (laws that give the inventor of a
new product the exclusive right to sell
it for
a certain period of time). Without laws
insisting on competition, many people
fear
that some firms would dominate others in
their industry and be able to charge consumers
any price. It is ironic that a philosophy that advocates no government regulation needs regulation to
remain viable.
You will recall from your study of American history that the 5th and 14th
amendments to the Constitution declare that no person may be deprived of “Life, liberty, or
property, without due process of law.” The 5th Amendment also says that “just
compensation” must be paid to owners when private property is taken for public use (eminent
domain). Private property is property that is owned by individuals or companies, not by the
government or the people as a whole. The Framers of the Constitution ensured that the United States
government would protect this fundamental right.
 | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
Adam Smith believed that government participation in the economy should
a. | be limited | c. | be promoted | b. | be forbidden | d. | be democratic |
|
|
|
5.
|
The authors believe that
a. | central planning is the most efficient method of providing economic and social
needs | c. | free markets can provide all of the economic and social needs of
society | b. | mixed economies are weak | d. | there are some social/economic needs that free markets are not able to
provide |
|
|
|
6.
|
The authors argue that free market capitalism needs ______ to guarantee that
markets remain competitive and free.
a. | the stock market | c. | money (investments) | b. | laws | d. | banks |
|
|
|
7.
|
What guarantees that Americans have a right to private property (property
rights)?
a. | The congress | c. | The U.S. Constitution | b. | The Declaration of
Independence | d. | The
president |
|
|
|
8.
|
From the quote above it is clear that Ronald Reagan believed in
a. | Socialism | c. | Capitalism | b. | Traditional Economies | d. | Communism |
|
|
|
Balancing Control and Freedom
A society must assess its
values and prioritize
its economic goals. Some goals are
better met by the open market and
others
are better met by government action. In
addition, societies must evaluate the
opportunity cost of pursuing each goal.
Each nation decides what it is willing to
give up to
meet its goals. What are you
willing to give up? Are you willing to pay
taxes to fund the army?
To give money to
people without jobs? To give all people an
education? To subsidize farms?
Should the
government establish job-safety guidelines
or a minimum wage? |
 | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
Societies have different economic goals.What economic factors do they have to
consider when deciding which goals to pursue?
a. | opportunity costs | c. | political power | b. | philosophical frameworks | d. | political
transparency |
|
|
|
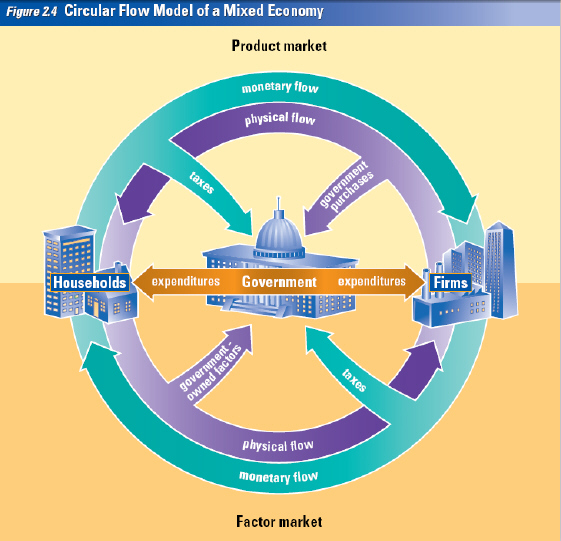 A
Circular Flow Model of a Mixed Economy
To illustrate the structure of most
modern
economies accurately, we need to add
government to our picture of the circular
flow
of economic activity. Figure 2.4 illustrates
the government’s role in the marketplace
in
a mixed economy. The government
can enter the circular flow of economic
activity in many
ways.
Government in the Factor Market
Just like
businesses, the government
purchases land, labor, and capital from
households in the factor
market. For
example, the United States government
pays 2.8 million employees $9.7 billion
a
year for their labor.
| Government in the Product Market
Governments purchase goods and
services
in the product market. They need buildings
and office supplies, telephones,
computers,
and fax machines, for example.
Governments also provide certain goods
and
services through the factor resources
that they combine. The federal, state, and
local
governments in the United States, for
example, provide 4 million miles of roads.
Transferring Money
As you can see from the outer ring
of
Figure 2.4, governments collect taxes
from both households and businesses.
Governments then
transfer the money they
collect to businesses and individuals for a
variety of reasons ranging
from worker
disability to the survival of an industry. The
greatest expenditure of the United
States
government is Social Security. | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
What does figure 2.4 above illustrate?
a. | poverty rates | c. | supply and demand | b. | government involvement in the
economy | d. | availability of
natural resources |
|
|
|
11.
|
In what way does the government participate in the product and factor
markets?
a. | award research grants to colleges and universities | c. | pay taxes to households and
businesses | b. | purchase of automobiles from General Motors | d. | collect taxes from households and
businesses |
|
|
|
12.
|
What is the biggest government expenditure?
a. | Social Security payments for retirement and disability | c. | interest on the
dept | b. | military spending | d. | government salaries |
|
|
|
13.
|
The government leases land to a company so they can drill for oil. This is an
example of
a. | government purchases | c. | government expenditures | b. | government owned
factors | d. | taxes |
|
|
|
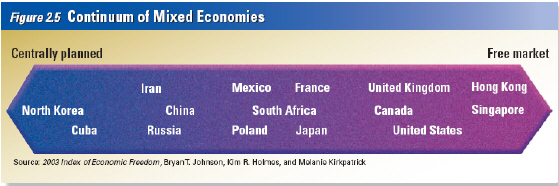 Comparing Mixed
Economies
The foundation of the United States economy is the free market. An economic
system characterized by private or corporate ownership of capital goods is called free enterprise.
In a free enterprise system investments are determined in a free market by private decision
rather than by state control. Figure 2.5 below shows a continuum of mixed economies. A continuum
is a range with no clear divisions. On one end of the scale is the centrally planned economy. On
the opposite end is the free market economy.
Mixed Economies
Where Government
Intervention Dominates
Reflecting an economy almost totally
dominated by the government, North Korea occupies one end of the scale. Government owns all the
property and all economic output. State-owned industries produce 95 percent of North Korea’s
goods. Almost all imports are banned, and production of goods and services by foreign companies is
forbidden.
In China, where the economy is dominated by government, one quarter of all
enterprises are at least partly owned by individuals. China, like many nations that have relied
heavily on central planning in the past, is in transition, a period of change in which an
economy moves away from central planning toward a | market-based system.
To make the transition, state firms must be privatized, or sold to individuals, and then
allowed to compete with one another in the marketplace. As you will read in Chapter 18, economic
transition is a difficult, and often painful, process.
Mixed
Economies Where the Market
System Dominates
At the other end of the scale, with one
of the
world’s freest markets, is Hong Kong. Hong
Kong, once administered by Great
Britain, is
now a special administrative region of China.
It continues, at the beginning of the
twenty first century, largely under the free economic
system it enjoyed under British
rule.
In Hong Kong, the private sector rules. The government protects private property and
rarely interferes in the free market, aside from establishing wage and price controls on rent and
some public services. It is highly receptive to foreign investment and imposes virtually no barriers
on foreign trade. Banks in Hong Kong operate independently of the government, and foreign-owned banks
have nearly all the same rights as domestic ones.
| | |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which country below has the freest markets?
a. | Mexico | c. | Singapore | b. | United States | d. | China |
|
|
|
15.
|
In which country does the government control all economic output, own all
property and bans all imports of foreign made goods and services?
a. | China | c. | Korea | b. | Australia | d. | Hong Kong |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the status of China in the continuum above?
a. | They are stuck in a centrally controlled market economy | c. | They are in
transition from a government controlled to a market controlled economy | b. | They are stuck in a
market controlled economy | d. | They are in transition from a market controlled to a government controlled
economy. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Why is it difficult to transition from a centrally controlled to a market
economy?
a. | Financial institutions do not like to deal in government securities | c. | There are seldom
enough citizens who want to participate in free markets | b. | Government assets
have to be sold or transferred to private individuals and companies | d. | There are not enough opportunity costs to make
the transition profitable |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which country provides the greatest economic opportunities for a small business
person?
a. | United States | c. | Hong Kong | b. | Mexico | d. | France |
|
|
|
 | The United States Economy
The United States
has a free enterprise economy. Still, the government intervenes to keep order, provide vital
services, and to promote the general welfare. Some people argue for more government services,
while others say that the government already intervenes too much in the economy. Nevertheless, the
United States enjoys a high level of economic freedom.
United States law protects private
property. The marketplace operates with a low level of government regulation. Foreign
investment is encouraged. So, too, is free trade, although the United States does protect some
domestic industries and does retaliate against trade restrictions imposed by other nations. The
banking industry operates under relatively few restrictions, and foreign-owned banks have few
additional restrictions. In the next chapter, you will read in detail about the government and the
free enterprise economy of the United States. | |
|
|
|
19.
|
The cartoon above is an argument for
a. | income distribution | c. | free markets | b. | price controls | d. | central
planning |
|
|
|
20.
|
What do the authors say about private property in the United States?
a. | They are protected by law | c. | The goal of the government is
property redistribution | b. | It has to be controlled because of its effect
on human rights | d. | property
rights are not supported in the Constitution |
|
|
|
21.
|
Laissez-Faire is a
a. | Liberal/Progressive philosophy | c. | Prohibitionist
Philosophy | b. | Libertarian/Conservative philosophy | d. | Communist
Philosophy |
|
|
|
22.
|
In the cartoon above, why did the pin store go out of business?
a. | Government controls placed on the pin business | c. | It cost more to produce the pins
than they were worth | b. | The free market was unfair to the pin
business | d. | The pins were too
cheap |
|
|
|
a. | continuum | d. | laissez faire | b. | private property | e. | privatize | c. | free
enterprise | f. | transition |
|
|
|
23.
|
an economic system characterized by private
or corporate ownership of capital goods; investments that are determined by private decision rather
than by state control; and determined in a free market
|
|
|
24.
|
period of change in which an economy moves
away from a centrally planned economy toward a market-based system
|
|
|
25.
|
the doctrine that states that government
generally should not intervene in the marketplace
|
|
|
26.
|
to sell state-run firms to
individuals
|
|
|
27.
|
a range with no clear
divisions
|
|
|
28.
|
property owned by individuals or companies, not by
the government or the people as a whole
|